Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Flaccidity is the reverse of turgidity.
Options
True
False
Solution
True
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption of water is called.
What is the difference between ‘flaccid’ and ‘turgid’? Give one example of flaccid condition in plants.
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Soaked seeds burst into three seed coats.
Differentiate between the following
Turgor pressure and Root pressure
The below diagram represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following: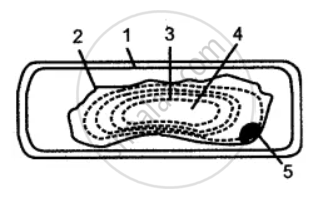
1. Cell wall
2. Plasma membrane.
3. Protoplasm
4. Large vacuole
5. Nucleus
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow :
(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) If the cell had been placed in distilled water instead of a strong sugar solution which features: would not have been present?
(iv) If the cell in the diagram possessed chloroplasts where would these be present?
(v) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
Name the following:
The condition in which the contents of a cell exert pressure against the cell wall making it distended.
Fill in the Blank
The condition opposite to turgid is ___________.
Multiple Choice Question:
When cell is fully turgid, which of the following will be zero?
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
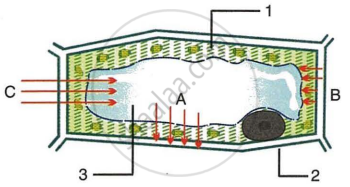
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
