Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment:

(i) Give the technical terms of the solutions used in beakers, 1, 2 and 3.
(ii) In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same. Explain the reason in brief.
(iii) Write the specific feature of the cell sap of root hairs which helps in absorption of water.
(iv) What is osmosis?
(v) How does a cell wall and a cell membrane differ in their permeability?
Solution
(i)
Solution 1 – Hypotonic solution
Solution 2 – Hypertonic solution
Solution 3 – Isotonic solution
(ii) In beaker three, the solution present is an isotonic solution, i.e. the relative concentration of water molecules and solutes is same in the solution as well as inside the cell. There is no movement of water molecules across the cell membrane. Hence, the size of the potato cubes remains same.
(iii) The cell sap of root hairs has higher concentration of solute than the surrounding water.
(iv) Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across the semi-permeable membrane from the region of dilute solution (i.e. a lower solute concentration) to the region of concentrated solution (i.e. a higher solute concentration).
(v) The cell wall is freely permeable to all the substances, while the cell membrane is selectively permeable and allows only certain substances to enter or exit the cell.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Movement of molecules of a substance from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration without the involvement a separating membrane, is called
Leaves of the sensitive plant wilt and droop down on a slight touch. What mechanism brings about this change?
The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
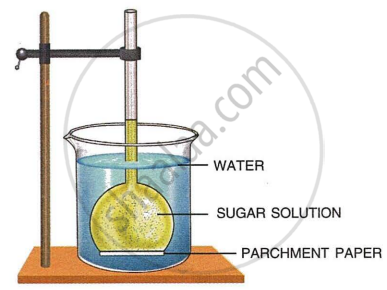
- Name the process.
- Define the above-named process.
- What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
- What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
- Keeping in mind the root hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to
- concentrated sugar solution
- parchment paper
- water in the beaker
- Name any other material that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.
- Mention two advantages of the process for the plants.
Two potato cubes each 1 cm3 in size, were placed separately in two containers (A&B), the container (A) having water and the other (B) containing concentrated sugar solution. After 24 hours when the cubes were examined, those placed in water were found to be firm and had increased slightly in size and those placed in concentrated sugar solution were found to be soft and had somewhat decreased in size. Use the above information to answer the questions that follow:
Account for the firmness and increase in the size of the potato cubes placed in water.
Define the following:
Hypertonic solution
Define the Cohesive and Adhesive forces.
Multiple Choice Question:
Osmosis involves:
Multiple Choice Question:
When a plant wilts, the sequence of events will be as follows:
Explain the Term: Diffusion
Explain the Term: Osmosis
