Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give Technical Term for the following.
A cell in a fully extended condition.
Solution
Turgid
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:

- What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
- Name the structure that acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- Label the parts numbered 1 to 4 in the diagram.
- How can the above cell be brought back to its original condition? Mention the scientific term for the recovery of the cell.
- State any two features of the above plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
A plant cell may burst when :
Give scientific reasons : Balsam plants wilt during mid-day even if the soil is well watered.
The diagram below represents a process in plants. The setup was placed in bright sunlight. Answer the following questions:

a) Name the physiological process depicted in the diagram.
Why was oil added to the water?
b) When placed in bright sunlight for four hours, what do you observe with regard to the initial and final weight of the plant? Give a suitable reason for your answer
c) What happens to the level of water when this setup is placed in:
- Humid conditions?
- Windy conditions?
d) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to overcome the process mentioned in (i).
e) Explain the term ‘Guttation’.
Give the equivalent terms for the following:
Loss of water through a cut stem.
Distinguish between the following:
Flaccid condition and turgid condition
Differentiate between:
Turgid and Flaccid.
Give the equivalent term for the following:
Pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
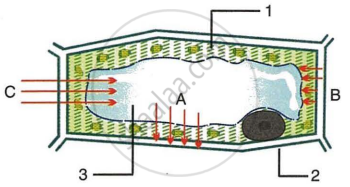
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
