Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Differentiate between:
Turgid and Flaccid.
Solution
| Sr. No. | Turgid | Flaccid |
| (i) | It occurs when the cell is placed in hypotonic solution. | It occurs when the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution. |
| (ii) | It occurs due to endosmosis. | It occurs due to exosmosis. |
| (iii) | The condition in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched due to the absorption of water is called turgidity. | The state in which the cell content is shrunken is called flaccidity. |
| (iv) | It is the state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by an increase in the volume of vacuoles due to the absorption of water. | It is the condition in which the cell content is shrunken and the cell is not tight. |
| (v) | Water moves into the cell. | Water moves out of the cell. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A plant cell may burst when :
Give the equivalent terms for the following:
Loss of water through a cut stem.
What is the difference between ‘flaccid’ and ‘turgid’? Give one example of flaccid condition in plants.
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
Name the following:
The process by which wilting or drooping of leaves occurs.
Fill in the Blank
Wilting and drooping of leaves is due to loss of ________.
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
Addition of salt to pickles is a method of killing the bacteria by ______.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
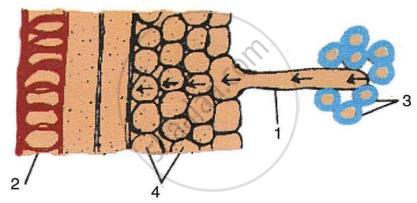
- The parts labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are:
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
- Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Root hair, Cortex respectively.
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Cortex, Soil particles respectively.
- Cortex, Soil particles, Xylem vessel, Root hair respectively.
- The process that enables the passage of water from soil into the root hair is:
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
- The kind of force which exists between a liquid and any surface is called as:
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Suction force
- The kind of force between the same kind of liquid molecules is:
- Capillary force
- Transpirational pull
- Adhesive force
- Cohesive force
- Sometimes exudation of water occurs from the margin of the leaves in the early morning or night. It is termed as:
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
- Osmosis
