Advertisements
Chapters
2: Fundamentals of Genetics
3: Absorption by Roots
4: Transpiration
5: Photosynthesis
▶ 6: The Circulatory System
7: The Excretory System
8: The Nervous System and Sense Organs
9: The Endocrine System
10: The Reproductive System
11: Human Population
12: Physical Health and Hygiene
13: Pollution
![ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 - The Circulatory System ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 - The Circulatory System - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: The Circulatory System
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE ICSE for Biology [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Short Questions
Why is circulatory system also known as transport system?
Write about origin and functions of Red Blood Corpuscles
Complete the following table:
| Components | Origin | Function | Approx. No. (mm3) | Life span |
| RBCs | ||||
| WBCs | ||||
| Platelets |
Define the following term:
Diapedesis
What are the functions of blood?
The table below is designed to indicate the transport of certain substances in our body. Fill in the blanks with suitable answers.
| Substance | From | To | |
| 1. | ______ | Lungs | Whole Body |
| 2. | Carbon Dioxide | ______ | ______ |
| 3. | Urea | ______ | ______ |
| 4. | Digested Carbohydrates | Intestines | ______ |
| 5. | ______ | ______ | Target Organs |
| 6. | Heat | ______ | Whole Body |
Why are capillaries thin walled?
Describe the role of lymph
Name the blood vessels entering the heart and leaving the heart.
Name the Blood vessels entering liver and kidney and Blood vessels leaving liver and kidney.
What does the term ‘double circulation’ mean?
In what ways does the blood entering the kidney differ from that leaving the kidney?
What is blood pressure?
How is blood pressure measured?
What is the value of systolic B. P. and diastolic B. P. of a normal human adult?
The table below is designed to indicate the major arteries emerging from the aorta and supplying blood to different organs.
Fill in the blanks with suitable answers.
| Name of the Artery | Supplying to | |
| (i) | Kidney | |
| (ii) | Genital | |
| (iii) | Right forelimb | |
| (iv) | Phrenic | |
| (v) | Liver | |
| (vi) | Chest |
Describe in brief die cardiac cycle.
When are the sounds ‘LUBB’ and ‘DUB’ produced during heartbeat ?
What is the Rh-factor?
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Give Reasons
Why is circulatory system also known as transport system?
Why do people have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest?
Veins have valves at intervals in their inner lining whereas the arteries do not have valves. Explain.
Why is the SA node called the pacemaker of the heart?
Why is it necessary to know the blood groups before giving transfusion?
Can the blood dot inside the blood vessels. Give reason in support of your answer.
Why does the number of leucocytes increase during infection?
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Differentiate
Differentiate between:
Blood and Lymph.
Differentiate between:
Arteries and Veins.
Differentiate between:
Red blood cells and White blood cells
Differentiate between:
Open circulatory system and Closed circulatory system.
Differentiate between:
Diastole and Systole.
Differentiate between:
Blood plasma and Serum.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Diagram Based Questions
Given alongside is a diagram of the external features of the heart.
(i) Name the parts ‘1’ to ‘7’.
(ii) What happens if the coronary artery gets an internal clot?
(iii) Which type of blood does part ‘5’ carry?
(iv) Mention one structural difference between part ‘5’ and ‘4’.
Given below is the simplified pathway of the circulatory system:
(i) Name the blood vessels marked 1 to 8.
(ii) Name the chamber of the heart which:
(a) Receives blood from ‘1’.
(b) Pumps blood into blood vessel ‘8’.
(iii) Mention two structural differences between blood vessels ‘7’ and ‘2’.
Given below is a schematic representation of the circulatory system in man. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Label the parts 1 to 4 indicated in the diagram.
(ii) Give one difference between parts 1 and 2 based on:
(a) their structure
(b) the nature of blood flowing through them.
(iii) What is the specific name of the type of blood circulation that takes place between the heart and the lungs?
(iv) Name the valve found at the beginning of the part labeled 3.
Given alongside is a highly diagrammatic sketch of the internal structure of the human heart:
(i) Name the parts numbered 1-11.
(ii) What is the main difference in the quality of blood contained in parts 6 and 7?
The diagram below represents the simplified pathway of the circulation of blood. Study the same and answer the questions which follow:

(i) Name the blood vessels labelled 1 and 2.
(ii) State the function of blood vessels labelled 5 and 8.
(iii) What is the importance of the blood vessel labelled 6?
(iv) Which blood vessel will contain a high amount of glucose and amino acids after a meal?
(v) Draw a diagram of the different blood cells as seen in a smear of human blood.
The figures given below are cross-sections of blood vessels.
(i) Identify the blood vessels A, B, and C.
(ii) Name the parts labeled 1-4.
(iii) Mention two structural differences between A and B.
(iv) Name the type of blood A that flows (a) through A, (b) through B.
(v) In which of the above vessels referred to in (iv) above does exchange of gases actually take place?
Given below is a simple diagram of the circulation of blood in a mammal showing the main blood vessels, the heart, lungs, and body tissues. The blood vessel labeled 6 contains deoxygenated blood and 2 the valve leading to it has three semi-lunar pockets.
(i) Name the blood vessels of organs marked by numbers 1 to 8.
(ii) What do you mean by the term ‘double circulation’ of blood in mammals?
(iii) What is diastole?
The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its activity. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
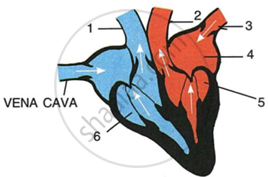 |
- Name the phase.
- Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
- Name the parts numbered 1to6.
- What type of blood flows through the parts marked 'l' and '2' respectively?
- How many valves are closed in this phase?
The figure below represents the internal structure of a mammalian heart and the associated blood vessels.
(i) (a) Name each of the structures labeled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.
(b) State the function of each of the structures 5, 6, 7, and 8.
(ii) (a) State the function of the heart as an entire organ.
(b) Why are the walls of the left ventricle more muscular than the right?
The diagrams given below show the cross-section of two kinds of blood vessels: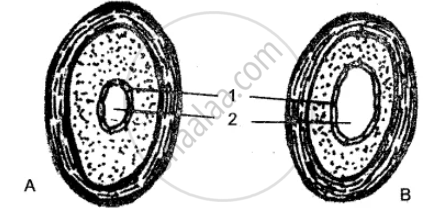
(i) Identify the blood vessels A and B. In each case give a reason to support your answer.
(ii) Name the parts numbered 1 and 2.
(iii) When are the sounds “LUBB” and “DUB” produced during a heartbeat?
(iv) Name the blood vessel that
(a) begins and ends in capillaries.
(b) supplies blood to the walls of the heart.
The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its functional activities. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the phase.
(ii) Label the parts 1, 2 and 3
(iii) Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase ? Give a reason to support your answer.
The diagram shows different types of blood cells, Name them.
A __________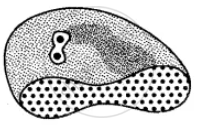
B ______________
C ____________
D _______________

E ____________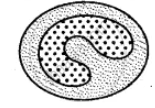
F ____________

G ______________
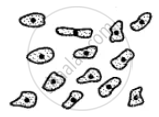
H ______________
The diagram below represents a certain category of blood vessels showing the role of a special structure in their walls :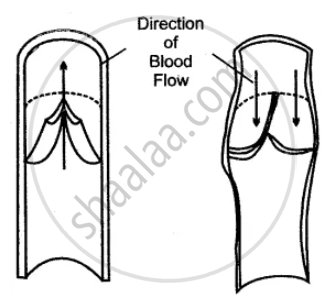
(i) Name the kind of blood vessels shown.
(ii) What is the structure shown inside the blood vessels?
(iii) What is the role of these structures?
(iv) Are these structures present in any other kind of blood vessel? If so, name it.
(v) Towards which side of the figure (Top or Bottom) is the heart located?
The diagram represents the ‘closed system’ or ‘double circulation’ of blood in mammals.
Justify the above statement.
State two structural and two functional differences between the arteries and veins.
State the changes in the composition of blood as it passes through the following organs:
(a) Lungs (b) Gut (c) Liver (d) Kidneys.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Sketch and Label the Diagram
Draw the diagram external features of the heart.
Draw the diagram of the Position of valves in the human heart.
Draw well labeled diagrams of part Artery and Superior vena cava to show the structural.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Explain the Terms
Explain the Term
Blood Pressure
Explain the Term
Pulse rate
Explain the Term
Double Circulation
Explain the Term
Hepatic Portal System
Explain the Term
Diapedesis
Explain the Term
Haemopoiesis
Explain the Term
Phagocytosis
Explain the Term
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Explain the Term
Pace maker
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Name the Following
Name the Following
The study of blood vascular system including arteries, veins and heart.
Name the Following
Number of chambers present in the human heart.
Name the Following
Layer, which surrounds the heart.
Name the Following
The blood vessel leaving the left ventricle of the mammalian heart
Name the Following
The valve present between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
Name the Following
The blood vessel supplying blood to the kidney.
Name the Following
The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries.
Name the Following
The blood vessels which have valves in them.
Name the Following
The fine blood vessels in the tissues through which exchange of materials occurs
Name the Following
The number of RBCs in men.
Name the Following
The instrument by which RBC are counted is called.
Name the Following
Oxygen is transported by the blood in the form of
Name the Following
The enzyme which converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Name the Following
The blood plasma from which fibrinogen has been removed.
Name the Following
By which the human body is protected from invading bacteria.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Give Technical Terms
Give Technical Term for the following:
What is the approximate weight of the heart of a man?
Give Technical Term for the following:
An unstable bright red compound formed between haemoglobin and oxygen to carry the oxygen to the body cells.
Name the following:
The artery which carries deoxygenated blood.
Give Technical Term for the following:
Name the vein in the human body which carries oxygenated blood.
Give Technical Term for the following:
Name the metallic element present in red blood cells.
Give Technical Term for the following:
The phase of cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract
Give Technical Term for the following:
The respiratory pigment contained in human blood.
The blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.
Name an instrument which is used to hear heart sounds.
The mineral element essential for the clotting of blood.
Name the following:
The process by which leucocytes engulf and destroy bacteria.
The soluble protein present in blood plasma responsible for blood clotting.
WBCs squeeze through the walls of the capillaries into the tissue.
The artificial method of filtering the blood or removing the wastes from the blood.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The iron pigment __________ gives red colour to the blood.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The ______ is the most powerful organ in the circulatory system.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The average heartbeat rate is ____ beats per minute in human being.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
In man (human), the heart has _____ chambers.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The erythrocytes contain an iron-rich pigment called __________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
Non-coagulation of blood is called ___________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
When oxygen is in fairly high concentration, the haemoglobin quickly combines with it and forms an unstable compound known as _______________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The element required for blood clotting is __________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
_________ helps in blood clotting.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate words:
The three distinct types of blood vessels are _____, ______, and _________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The site of production of W.B.Cs in the embryo is _________
Complete the following sentence with appropriate words:
The _______ is referred to as the graveyard of red blood corpuscles and the _______ referred to as the cradle of red blood corpuscles.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate words:
The red blood corpuscles are ________ and _____ shaped cells without ________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The fluid in the space between the tissue cell is called__________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The foundations of physiology were laid by the physician __________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
Beside food, oxygen and waste materials, circulatory system transports ________ to various parts of the body.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
__________ are the blood vessels which usually carry oxygenated blood.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The chamber of heart which pumps blood into aorta is __________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate words:
Arteries are _____ walled and the veins are _____ walled vessels.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The blood vessel which transports blood from heart to an organ is called _________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The sequence of one systole followed by one diastole is termed as the ___________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The membranous covering of the heart is _______.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The heart is made up of special muscles, the _______ muscles.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the _________.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
The blood vessel leaving the left ventricle of the mammalian heart is the _________.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System True & False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
The heart of a normal human adult beats more than one lakh times per day.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
W.B.C. contains haemoglobin
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
R.B.Cs are of several kinds whereas WBCs are of one kind.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Leucocytes show amoeboid movement.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
The average life of red blood cells in our body is about 120 hours.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Serum is an immunological preparation of blood (without cells and fibrinogen) containing antibodies and antitoxins against specific diseases
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Blood group AB is universal donor.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
The walls of auricles are thicker than those of ventricles.
True
False
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System State the Location
State the Location: Hepatic portal vein
State the Location:
Tonsils
State the Location: Spleen
State the Location: Sino-auricular node
State the Location: Bicuspid value
State the Location: Pulmonary vein
State the Location: Semilunar valves of the heart
State the Location: Bundle of His
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System State the Function
State the Function: Pulmonary vein
State the Function: Thrombocytes
State the Function: Semilunar valves of the heart
State the Function: Bundle of His
State the Function: Coronary artery
State the Function: Bicuspid valve
State the Function: Haemoglobin
State the Function: Vitamin K
State the Function: Pericardium
State the Function: Pulmonary artery
State the Function: Lymph
State the Function: W.B.C.
State the Function: R.B.C.
State the Function: Platelets
State the Function: Tricuspid valve
State the Function: Chordae tendinae
State the Function: Vena cava
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out:
Human heart
Fish heart
Reptile heart
Toad heart
Choose the Odd One Out:
Artery
Vein
Portal vein
Lacteal
Choose the Odd One Out:
RBC
ATP
WBC
Platelets
Choose the Odd One Out:
Purkinje fibres
A. V. node
A. V. valve
S. A. node
Choose the Odd One Out:
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Semilunar valve
Venous valve
Choose the Odd One Out:
Systolic pressure
Diastolic pressure
Stethoscope
Sphygmomanometer
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
The function of WBC is:
To distribute heat
To protect enzymes
To cause blood clotting
To destroy bacteria
Multiple Choice Questions
Agranulocytes are:
Lymphocytes, monocytes
Lymphocytes, basophils
Eosinophils, basophils
Eosinophils, monocytes
Multiple Choice Questions
The chief function of lymph nodes in mammals is to:
Produce WBCs
Produce hormones
Destroy old RBCs
Destroy pathogens
Multiple Choice Questions
What will happen if the spleen of a man is removed?
W.B.C. production will be lowered
Removal of dead RBC will not take place
Antibody production will be decreased
R.B.C. production will be stopped
Multiple Choice Questions
Which protein is used in preventing clotting of blood?
Albumin
Heparin
Fibrinogeri
Globulin
Multiple Choice Questions
The beating of the heart of man is heart on the left side, because:
The left ventride is towards the left side
Both the ventricles are towards the left side
Contraction of heart is powerful on left side
The dorsal aorta is on the left side
Multiple Choice Questions
Arteries are:
Thin walled and blood flows under diminished pressure
Thick walled and blood flows under high pressure
Thin walled and blood flows under low pressure
Thick walled and blood flows under diminished pressure
Multiple Choice Questions
What is blood pressure?
The pressure of blood on the heart muscles
The pressure of blood exerted on the walls of arteries and veins
The pressure of blood on the walls of veins only
The pressure of blood on the walls of arteries only
Multiple Choice Questions
Erythroblastosis foetalis can occur when:
Man Rh+ve and woman Rh+ve
Man Rh-ve and woman Rh+ve
Man Rh+ve and woman Rh-ve
Man Rh-ve and woman Rh-ve
Multiple Choice Questions
Blood pressure is measured by:
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Stethoscope
Sphygmomanometer
Pulse rate
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 6 The Circulatory System Match the Columns
Column 2 is a list of items related to ideas in Column 1. Match the term in Column 2 with the suitable idea given in Column 1.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| (i) Superior vena cava | (a) Collect deoxygenated blood from the wall of the heart. |
| (ii) Inferior vena cava | (b) Carry oxygenated blood to heart muscle. |
| (iii) Pulmonary vein | (c) Collects deoxygenated blood from upper part. |
| (iv) Coronary veins | (d) Collects deoxygenated blood from lower parts. |
| (v) Coronary artery | (e) Brings oxygenated blood from lungs. |
| (vi) Aorta | (f) Large artery |
| (vii) Heart attack | (g) Large vein |
| (viii) Blood Pressure | (h) Oxygenated blood |
| (ix) Tricuspid valve | (i) Sphygmomanometer |
| (x) Bicuspid valve | (j) Allows blood flow from right auricle to right ventricle. |
| (xi) Contraction and relaxation of heart | (k) Blocking of coronary arteries. |
| (l) Cardiac muscle. | |
| (m) Allows blood flow from left auricle to left ventricle. | |
| (n) Allows blood flow from right ventricle of pulmonary aorta. |
Solutions for 6: The Circulatory System
![ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 - The Circulatory System ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 - The Circulatory System - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 - The Circulatory System
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE 6 (The Circulatory System) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 6 The Circulatory System are Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes), Blood Circulatory System in Human, Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart), Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation), Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system), Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP", Working mechanism of human heart, Pacemaker, Blood Vessels, Blood Pressure (B.P.), Tissue Fluid (Or Intercellular Fluid), Lymph and Lymphatic System, The Spleen, Circulation in Animals, Fluids in Our Body, Blood, Functions of Blood, Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood), Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes), Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Human Heart, Types of Closed Circulation.
Using ICSE Biology [English] Class 10 solutions The Circulatory System exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Biology [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, The Circulatory System Biology [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
