Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After sometime, it assumed a shape as shown below:
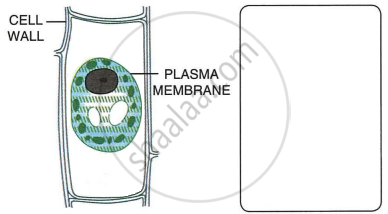
- Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
- Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
- Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
- Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
Solution
- Flaccid Cell (Plasmolysis)
- Plasma membrane
- Hypertonic solution
- Presence of cell wall

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The state of a cell in which the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption of water is called.
Differentiate between the following:
Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Differentiate between the following:
Turgidity and Flaccidity
What is the difference between ‘flaccid’ and ‘turgid’? Give one example of flaccid condition in plants.
Give reasons for the following:
If you sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at that spot.
Distinguish between the following:
Flaccid condition and turgid condition
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
Name the following:
The process by which wilting or drooping of leaves occurs.
Fill in the Blank
Wilting and drooping of leaves is due to loss of ________.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
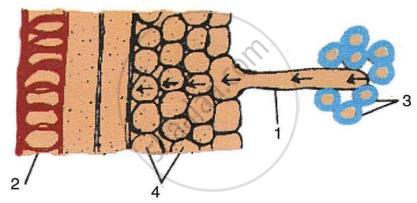
- The parts labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are:
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
- Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Root hair, Cortex respectively.
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Cortex, Soil particles respectively.
- Cortex, Soil particles, Xylem vessel, Root hair respectively.
- The process that enables the passage of water from soil into the root hair is:
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
- The kind of force which exists between a liquid and any surface is called as:
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Suction force
- The kind of force between the same kind of liquid molecules is:
- Capillary force
- Transpirational pull
- Adhesive force
- Cohesive force
- Sometimes exudation of water occurs from the margin of the leaves in the early morning or night. It is termed as:
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
- Osmosis
