Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
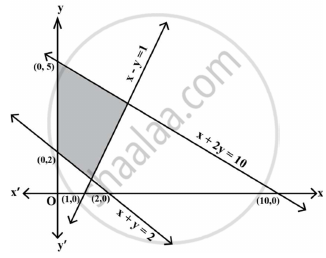
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
विकल्प
x + y ≥ 2
x + 2y ≤ 10
x – y ≥ 1
x – y ≤ 1
उत्तर
x – y ≥ 1
Explanation:
We observe, (0, 0) does not satisfy the inequality x – y ≥ 1
So, the half plane represented by the above inequality will not contain origin
Therefore, it will not contain the shaded feasible region.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Minimize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to the conditions:
3x + 2y ≥ 12,
x + y ≥ 5,
0 ≤ x ≤ 4,
0 ≤ y ≤ 4
Minimize :Z=6x+4y
Subject to : 3x+2y ≥12
x+y ≥5
0 ≤x ≤4
0 ≤ y ≤ 4
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B'. 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs Rs 10 per kg and 'B' cost Rs 8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y
Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24
3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 5y
Subject to
\[x + 2y \leq 20\]
\[x + y \leq 15\]
\[ y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
A company produces two types of leather belts, say type A and B. Belt A is a superior quality and belt B is of a lower quality. Profits on each type of belt are Rs 2 and Rs 1.50 per belt, respectively. Each belt of type A requires twice as much time as required by a belt of type B. If all belts were of type B, the company could produce 1000 belts per day. But the supply of leather is sufficient only for 800 belts per day (both A and B combined). Belt A requires a fancy buckle and only 400 fancy buckles are available for this per day. For belt of type B, only 700 buckles are available per day.
How should the company manufacture the two types of belts in order to have a maximum overall profit?
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A firm manufactures two products A and B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. Product A requires 4 minutes of processing time on M1 and 8 min. on M2 ; product B requires 4 minutes on M1 and 4 min. on M2. The machine M1 is available for not more than 8 hrs 20 min. while machine M2 is available for 10 hrs. during any working day. The products A and B are sold at a profit of Rs 3 and Rs 4 respectively.
Formulate the problem as a linear programming problem and find how many products of each type should be produced by the firm each day in order to get maximum profit.
A factory uses three different resources for the manufacture of two different products, 20 units of the resources A, 12 units of B and 16 units of C being available. 1 unit of the first product requires 2, 2 and 4 units of the respective resources and 1 unit of the second product requires 4, 2 and 0 units of respective resources. It is known that the first product gives a profit of 2 monetary units per unit and the second 3. Formulate the linear programming problem. How many units of each product should be manufactured for maximizing the profit? Solve it graphically.
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A small firm manufacturers items A and B. The total number of items A and B that it can manufacture in a day is at the most 24. Item A takes one hour to make while item B takes only half an hour. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. If the profit on one unit of item A be Rs 300 and one unit of item B be Rs 160, how many of each type of item be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
A firm makes items A and B and the total number of items it can make in a day is 24. It takes one hour to make an item of A and half an hour to make an item of B. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. The profit on an item of A is Rs 300 and on one item of B is Rs 160. How many items of each type should be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
A box manufacturer makes large and small boxes from a large piece of cardboard. The large boxes require 4 sq. metre per box while the small boxes require 3 sq. metre per box. The manufacturer is required to make at least three large boxes and at least twice as many small boxes as large boxes. If 60 sq. metre of cardboard is in stock, and if the profits on the large and small boxes are Rs 3 and Rs 2 per box, how many of each should be made in order to maximize the total profit?
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers a desktop model and a portable model that will cost Rs 25,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than Rs 70 lakhs and his profit on the desktop model is Rs 4500 and on the portable model is Rs 5000. Make an LPP and solve it graphically.
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at ₹7 profit and that of B at a profit of ₹4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
A medical company has factories at two places, A and B. From these places, supply is made to each of its three agencies situated at P, Q and R. The monthly requirements of the agencies are respectively 40, 40 and 50 packets of the medicines, while the production capacity of the factories, A and B, are 60 and 70 packets respectively. The transportation cost per packet from the factories to the agencies are given below:
| Transportation Cost per packet(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| P | 5 | 4 |
| Q | 4 | 2 |
| R | 3 | 5 |
Find the graphical solution for the system of linear inequation 2x + y ≤ 2, x − y ≤ 1
The maximum value of z = 6x + 8y subject to x - y ≥ 0, x + 3y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The maximum value of Z = 5x + 4y, Subject to y ≤ 2x, x ≤ 2y, x + y ≤ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem: Max P = 2x + 3y subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 2y ≤ 9, 2x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 8, is ______
Corner points of the feasible region determined by the system of linear constraints are (0, 3), (1, 1) and (3, 0). Let Z = px + qy, where p, q > 0. Condition on p and q so that the minimum of Z occurs at (3, 0) and (1, 1) is ______.
Z = 20x1 + 20x2, subject to x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, x1 + 2x2 ≥ 8, 3x1 + 2x2 ≥ 15, 5x1 + 2x2 ≥ 20. The minimum value of Z occurs at ____________.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
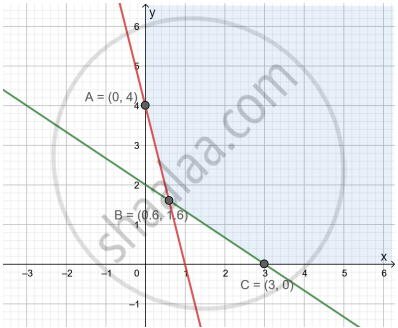
The corner points of the shaded unbounded feasible region of an LPP are (0, 4), (0.6, 1.6) and (3, 0) as shown in the figure. The minimum value of the objective function Z = 4x + 6y occurs at ______.
The objective function Z = x1 + x2, subject to the constraints are x1 + x2 ≤ 10, – 2x1 + 3x2 ≤ 15, x1 ≤ 6, x1, x2 ≥ 0, has maximum value ______ of the feasible region.
If x – y ≥ 8, x ≥ 3, y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 then find the coordinates of the corner points of the feasible region.
A linear programming problem is given by Z = px + qy where p, q > 0 subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 60, 5x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
- Solve graphically to find the corner points of the feasible region.
- If Z = px + qy is maximum at (0, 60) and (10, 50), find the relation of p and q. Also mention the number of optimal solution(s) in this case.
