Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The functional group which always occurs in the middle of a carbon chain is:
(a) alcohol group
(b) aldehyde group
(c) carboxyl group
(d) ketone group
उत्तर
ketone group
The ketone group (-CO-), with the general formula R-CO-R, is always present in the middle of a carbon chain.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the name and general formula of a chain of hydrocarbons in which an addition reaction with hydrogen is possible. State the essential condition for an addition reaction. Stating this condition, write a chemical equation giving the name of the reactant and the product of the reaction.
Draw the structures of possible isomers of butane, C4H10.
Explain the meaning of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
You are given the following molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons:
C5H8; C7H14; C6H6; C5H10; C7H12; C6H12
Which three formulae represent open chain unsaturated hydrocarbons having double bonds?
Draw two possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and write their names.
Give the electron dot structures of the above two compounds.
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{C - H}\\
\phantom{.........}|\\
\phantom{.........}\ce{H}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H - C - H}\\
|\\\ce{H}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}
\end{array}\]
Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in column (B).
| Column (A) | Column (B) | ||
(a) |
`"CH"_3"OH" + "CH"_3"COOH"overset("H"^+)(->) "CH"_3"COOCH"_3 + "H"_2"O"` | (i) | Addition reaction |
| (b) | `"CH"_3 = "CH"_2 + "H"_2 overset("Ni")(->)"CH"_3 - "CH"_3` | (ii) | Substitution reaction |
| (c) | `"CH"_4 + "Cl"_2overset("Sunlight")(->)"CH"_3"Cl" + "HCl"` | (iii) | Neutralisation reaction |
| (d) | `"CH"_3"COOH" + "NaOH" -> "CH"_3"COONa" + "H"_2"O"` | (iv) | Esterification reaction |
How will you prove that C4H8 and C5H10 are homologues?
Name the following:
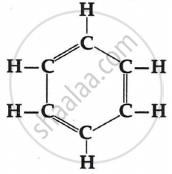
Draw the structure of propanone.
