Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the meaning of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
उत्तर
(1) Saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are connected by single bonds only. They are also called alkanes, and their general formula is CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in each of their molecules.
Examples: Methane (CH4) and butane (C4H10) are saturated hydrocarbons with 1 and 4 carbon atoms respectively, and their names end with 'ane'. The atoms are only connected by single covalent bonds.
The structures are represented below

2) Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which two carbon atoms are either connected by a double bond or triple bond. If the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond, then it is called an alkene, and its general formula is CnH2n.
Example: Ethene (C2H4) is an alkene in which two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond.
The structure is as follows:
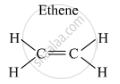
If two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond, then it is called an alkyne, and its general formula is CnH2n-2.
Example: Ethyne (C2H2) is an alkyne in which two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond.
The structure of ethyne is as follows:

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The property of carbon atoms to form long chains in compounds is called ...........
Write the molecular formula and structure of benzene.
Two organic compounds A and B have the same molecular formula C6H12. Write the names and structural formulae:
Which compound contains only single bonds?
You are given the following molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons:
Which formula represents benzene?
You are given the following molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons:
C5H8; C7H14; C6H6; C5H10; C7H12; C6H12
Which three formulae represent open chain unsaturated hydrocarbons having double bonds?
What is the molecular formula and structural formula of a cyclic hydrocarbon whose one molecule contains 8 hydrogen atoms?
Draw two possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and write their names.
Give the electron dot structures of the above two compounds.
A reagent which can help us to distinguish between alkenes and alkynes is ______.
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{C - H}\\
\phantom{.........}|\\
\phantom{.........}\ce{H}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H - C - H}\\
|\\\ce{H}
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}
\end{array}\]
Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in column (B).
| Column (A) | Column (B) | ||
(a) |
`"CH"_3"OH" + "CH"_3"COOH"overset("H"^+)(->) "CH"_3"COOCH"_3 + "H"_2"O"` | (i) | Addition reaction |
| (b) | `"CH"_3 = "CH"_2 + "H"_2 overset("Ni")(->)"CH"_3 - "CH"_3` | (ii) | Substitution reaction |
| (c) | `"CH"_4 + "Cl"_2overset("Sunlight")(->)"CH"_3"Cl" + "HCl"` | (iii) | Neutralisation reaction |
| (d) | `"CH"_3"COOH" + "NaOH" -> "CH"_3"COONa" + "H"_2"O"` | (iv) | Esterification reaction |
