Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the meaning of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
Solution
(1) Saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms are connected by single bonds only. They are also called alkanes, and their general formula is CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in each of their molecules.
Examples: Methane (CH4) and butane (C4H10) are saturated hydrocarbons with 1 and 4 carbon atoms respectively, and their names end with 'ane'. The atoms are only connected by single covalent bonds.
The structures are represented below

2) Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons in which two carbon atoms are either connected by a double bond or triple bond. If the two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond, then it is called an alkene, and its general formula is CnH2n.
Example: Ethene (C2H4) is an alkene in which two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond.
The structure is as follows:
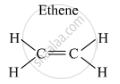
If two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond, then it is called an alkyne, and its general formula is CnH2n-2.
Example: Ethyne (C2H2) is an alkyne in which two carbon atoms are connected by a triple bond.
The structure of ethyne is as follows:

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the structures for Bromopentane*
Draw the structures for Hexanal.
The number of carbon atoms in the organic compound named as 2,2-dimethylpropane is:
(a) two
(b) five
(c) three
(d) four
Write the molecular and structural formula of a cyclic hydrocarbon whose molecule contains 8 atoms of carbon.
Three organic compounds A, B and C have the following molecular formulae: C4H8O
Which molecular formula can represent an aldehyde as well as a ketone? Write the names and structural formulae of the aldehyde and ketone represented by this molecular formula.
Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12. It has ______.
Hydrocarbons are mainly composed of which of these?
Intake of small quantity of methanol can be lethal. Comment.
Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in column (B).
| Column (A) | Column (B) | ||
(a) |
`"CH"_3"OH" + "CH"_3"COOH"overset("H"^+)(->) "CH"_3"COOCH"_3 + "H"_2"O"` | (i) | Addition reaction |
| (b) | `"CH"_3 = "CH"_2 + "H"_2 overset("Ni")(->)"CH"_3 - "CH"_3` | (ii) | Substitution reaction |
| (c) | `"CH"_4 + "Cl"_2overset("Sunlight")(->)"CH"_3"Cl" + "HCl"` | (iii) | Neutralisation reaction |
| (d) | `"CH"_3"COOH" + "NaOH" -> "CH"_3"COONa" + "H"_2"O"` | (iv) | Esterification reaction |
Draw the structure of propanone.
