Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The resistance of a conductivity cell with a 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 ohm. When the same cell is filled with a 0.02 M NaCl solution, the resistance is 1100 ohm. If the conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1, calculate the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl solution.
उत्तर
Given: `"R"_((0.1 "M" "KCl"))` = 200 ohm, `"R"_((0.02 "M" "NaCl"))` = 1100 ohm
`"K"_((0.1 "M" "KCl"))` = 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1
`"G"_((0.02 "M" "NaCl"))` = ?, ∧m = ?
Cell constant (G) = Conductivity (K) × Resistance (R)
= 200 × 0.0129
= 2.58 cm-1
Conductivity `(lambda_(0.02 "M" "NaCl")) = "Cell constant (G)"/("Resistance" ("R"_(0.02 "M" "NaCl")))`
`= (2.58)/1100`
= 2.345 × 10-3 s cm-1
Molar conductivity (λm) `= "Conductivity (K) × 1000"/"Molarity"`
`= (2.345 xx10^-3 xx 1000)/(0.02)`
= 117.25 s m2 mol-1
Hence, the cell constant and moral conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl will be 2.345 × 10-3 s cm-1 and 117.25 s m2 mol-1, respectively.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define "Molar conductivity".
State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
The molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L−1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol−1. Calculate its degree of dissociation and dissociation constant. Given \[\ce{λ^0_{(H^+)}}\] = 349.6 S cm2 mol−1 and \[\ce{λ^0_{(HCOO^-)}}\] = 54.6 S cm2 mol−1.
The conductivity of sodium chloride at 298 K has been determined at different concentrations and the results are given below:
| Concentration/M | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.050 | 0.100 |
| 102 × κ/S m−1 | 1.237 | 11.85 | 23.15 | 55.53 | 106.74 |
Calculate `∧_"m"`for all concentrations and draw a plot between `∧_"m"`and `"c"^(1/2)`. Find the value of `∧_"m"^0`.
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
Molar conductivity denoted by the symbol Λm is related to the conductivity of the solution by the equation (k is the conductivity and c is the concentration).
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
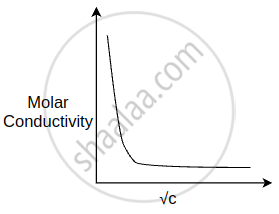
The electrolyte X is ______.
