Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The specific heat capacity of a body depends on _____________ .
विकल्प
the heat given
the temperature raised
the mass of the body
the material of the body
उत्तर
the material of the body
Heat capacity of a body is due to their material properties. Due to different molecular structures, different bodies have a different capacity to absorb heat. Therefore, specific heat of a body depends on the material of the body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
You have a choice of three metals A, B, and C, of specific heat capacities 900 Jkg-1 °C-1, 380 Jkg-1 °C-1 and 460 Jkg-1 °C-1 respectively, to make a calorimeter. Which material will you select? Justify your answer.
What do you understand by the following statements:
The specific heat capacity of lead is 130 Jkg-1K-1.
Heat supplied to a solid change it into liquid. What is this change in the phase called?
Give a mathematical relation between Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity.
The temperature of 170 g of water at 50°C is lowered to 5°C by adding a certain amount of ice to it. Find the mass of ice added.
Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1 and specific latent heat of ice = 336000 J kg-1.
The specific heat capacity of water is :
What is meant by global warming?
What impact will global warming have on the health of the affected population?
Who shall pay carbon tax ?
Which principle is used to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance?
650 J of heat is required to raise the temp. of 0.25 kg of lead from 15°C to 35°C. Calculate the Sp. heat capacity of lead.
State, with reason, which of the two, boiling water or steam both at 100°C will produce more severe burns.
Fill in the following blank using suitable word:
SI unit of heat is .........
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
Explain, why does a wise farmer water his fields, if forecast is forst?
The temperature of a lead piece of mass 400 g rises from 20°C to 50°C when 1560 J of heat is supplied to it. Calculate: Heat capacity of lead piece.
The temperature of a lead piece of mass 400 g rises from 20°C to 50°C when 1560 J of heat is supplied to it. Calculate Specific heat capacity of lead.
Water falls from a height of 50 m. Calculate the rise in the temperature of water when it strikes the bottom.
(g = 10 ms-2; Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J / kg°C)
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
A. hot solid of mass 60 g at 100°C is placed in 150 g of water at 20° C. The final steady temperature recorded is 25°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the solid. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1]
A vessel of negligible heat*capacity contains 40g of ice in it at 0°C, 8g of steam at 100°C is passed into the ice to melt it. Find the final temperature of the contents of the vessel.
(Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2268 J/g, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/f and specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g°C)
The molar specific heat of a gas at constant volume is 12307.69 J kg-1 K-1. If the ratio of the two specific heats is 1.65, calculate the difference between the two molar specific heats of gas.
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
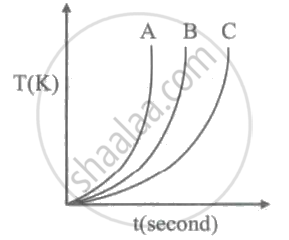
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
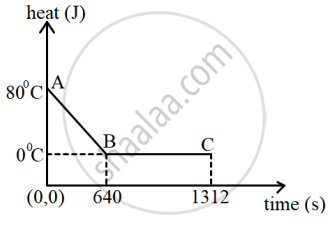
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Specific heat capacity C = ______.
The specific heat capacity of water is ______.
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| 1. | Specific heat capacity of water | a. | 0°C |
| 2. | Latent heat of fusion of ice | b. | 2260 J/g |
| 3. | Latent heat of vaporization of water | c. | 100°C |
| 4. | The melting point of iced | d. | 4.2 J/g°C |
| 5. | The boiling point of water | e. | 336 J/g |
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific heat?

To study energy exchange between hot and cold objects, the system of both objects is isolated from the environment by keeping them inside ______.
Match the columns:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| The SI unit of specific heat capacity | (a) Jkg−1°C−1 |
| (b) kg/m3 | |
| (c) calorie |
The specific heat capacity of ______ is maximum.
A geyser heats water flowing at a rate of 2.0 kg per minute from 30°C to 70°C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, the rate of combustion of fuel will be ______ g min-1.
[Heat of combustion = 8 × 103 Jg-1 Specific heat of water = 4.2 Jg-1°C-1]
Two blocks P and Q of different metals having their mass in the ratio 2 : 1 are given same amount of heat. Their temperature rises by same amount. Compare their specific heat capacities.
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 200 g of copper from 20°C to 70°C. Specific heat capacity of copper = 390 J kg-1 K-1.
