Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The specific heat capacity of a body depends on _____________ .
पर्याय
the heat given
the temperature raised
the mass of the body
the material of the body
उत्तर
the material of the body
Heat capacity of a body is due to their material properties. Due to different molecular structures, different bodies have a different capacity to absorb heat. Therefore, specific heat of a body depends on the material of the body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define heat capacity and state its SI unit.
A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20°C to ice at -10°C in 35 minutes. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in terms of watts.
Given: Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1°C-1
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1K-1 whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1
(i) Which of the two is a good conductor of heat?
(ii) How is one led to the above conclusion?
(iii) If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Differentiate between heat capacity and specific heat capacity.
A mass m1 of a substance of specific heat capacity c1 at temperature t1 is mixed with a mass m2 of other substance of specific heat capacity c2 at a lower temperature t2. Deduce the expression for the temperature t of the mixture. State the assumption made, if any.
Explain the term boiling point ?
Ice cream appears colder to the mouth than water at 0℃. Give reason.
Give three reasons for the increase of green house gases.
State the effect of enhancement of green house effect.
Indian style of cooling drinking water is to keep it in a pitcher having porous walls. Water comes to the outer surface very slowly and evaporates. Most of energy needed for evaporation is taken from the water itself and the water is cooled down. Assume that a pitcher contains 10 kg of water and 0.2 g of water comes out per second. Assuming no backward heat transfer from the atmosphere to the water, calculate the time in which the temperature decrease by 5°C. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1.
104g of water at 30°C is taken in a calorimeter made of copper of mass 42 g. When a certain mass of ice at 0°C is added to it, the final steady temperature of the mixture after the ice has melted, was found to be 10°C. Find the mass of ice added. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg–1°C–1 ; Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg–1; Specific heat capacity of copper = 0.4 Jg–1°C–1] .
(b) 2000 J of heat energy is required to raise the temperature of 4 kg of a
metal by 3°c. Which expression gives the specific heat capacity of the metal?
A solid of mass 80 g at 80°C is dropped in 400 g water at 10°C. If final temp. is 30°C, find the sp. heat cap. of the solid.
State, with reason, which of the two, boiling water or steam both at 100°C will produce more severe burns.
A liquid X has specific heat capacity higher than the liquid Y. Which liquid is useful as coolant in car radiators.
Name the substance which has maximum specific heat capacity.
Write two advantages of high specific heat capacity of water.
Write the approximate values of the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam.
Explain, why is water sprayed on roads in evening in hot summer?
Explain, why do sandy soils, get heated up quickly as compared to wet soils?
If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Given: Specific heat capacity’A’ 3.8 J/g /K. Specific heat capacity ‘B’ 0.4 J/g /K.
Describe a method to determine the specific heat capacity of a solid (say, a piece of copper).
Discuss how high specific heat capacity of water helps in formation of land and sea breeze.
A piece of ice is heated at a constant rate. The variation of temperature with heat input is shown in the graph below:

(i) What are represented by AB and CD?
(ii) What conclusion can you draw regarding the 110°c nature of ice from the above graph?
A vessel of negligible heat*capacity contains 40g of ice in it at 0°C, 8g of steam at 100°C is passed into the ice to melt it. Find the final temperature of the contents of the vessel.
(Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2268 J/g, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/f and specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g°C)
Solve the following problem.
Specific latent heat of vaporization of water is 2.26 × 106 J/kg. Calculate the energy needed to change 5.0 g of water into steam at 100 ºC.
Calculate the ratio of two specific heats of polyatomic gas molecules.
Define specific heat capacity.
50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10° C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 5 g water, the rise in its temperature is [Specific heat of copper = 420 joule-kg-1 °C-1 , specific heat of water = 4200 joule-kg-I °C-1]
Which of the substances P, Q, or R has the lowest specific heat? The temperature v/s time graph is shown ______.

On supplying 100 µC of charge to a conductor, its potential rises by 5 V then capacity of the conductor is ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
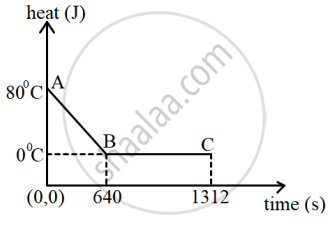
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Conductors have generally high specific heat capacities and insulators have low specific heat capacities.
Two cylinders of equal height and radius are made of copper and aluminum. Which of them conducts heat faster?
To study energy exchange between hot and cold objects, the system of both objects is isolated from the environment by keeping them inside ______.
Two blocks P and Q of different metals having their mass in the ratio 2 : 1 are given same amount of heat. Their temperature rises by same amount. Compare their specific heat capacities.
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 200 g of copper from 20°C to 70°C. Specific heat capacity of copper = 390 J kg-1 K-1.
