Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below:
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
उत्तर
The plot between voltage and current is called IV characteristic. The voltage is plotted on x-axis and current is plotted on y-axis. The values of the current for different values of the voltage are shown in the given table.
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
The IV characteristic of the given resistor is plotted in the following figure.
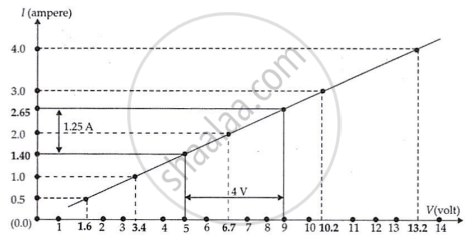
For V = 4 V (i.e., 9 V − 5 V)
I = 1.25 A (i.e., 2.65 A − 1.40 A).
∴ `"R" = "V"/"I"`
= `(4 "V")/(1.25 "A")`
= 3.2 Ω
The accuracy of the graph's plotting determines the value of R that is found on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The values of current (I) flowing through a given resistor of resistance (R), for the corresponding values of potential difference (V) across the resistor are as given below:
| V (volts) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 |
| I (amperes) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Plot a graph between current (I) and potential difference (V) and determine the resistance (R) of the resistor.
Which of the following statements correctly defines a volt?
(a) a volt is a joule per ampere.
(b) a volt is a joule per coulomb.
Define one coulomb charge.
What do you understand by the term "potential difference"?
How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Name the law which relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.
Define the unit of resistance (or Define the unit "ohm").
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become:
Calculate the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits: a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
The V-I graph for a series combination and for a parallel combination of two resistors is shown in Fig – 8.38. Which of the two, A or B, represents the parallel combination? Give a reason for your answer.
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph.)
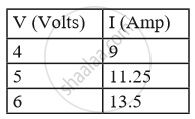
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.

Suppose there are three resistors A, B, and C having resistances r1, r2, and r3 respectively. If R represents their equivalent resistance, establish the following relation `1/"R" = 1/"r"_1 + 1/"r"_2 + 1/"r"_3`, when joined in parallel.
A 10 m long wire of a particular material is of resistance 5Ω What will be the resistance if the wire is stretched to double its length?
Which of the following represents voltage?
Electric potential is a ____________.
A cylindrical conductor of length l and uniform area of cross section A has resistance R. Another conductor of length 2l and resistance R of the same material has area of cross section
Electric potential is a measure of the ______ on the unit positive charge to bring it to that point against all electrical forces.
Twenty-seven drops of same size are charged at 220 V each. They combine to form a bigger drop. Calculate the potential of the bigger drop.
