Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The vertices of a triangle are O (0, 0), A (a, 0) and B (0, b). Write the coordinates of its circumcentre.
उत्तर
The coordinates of circumcentre of a triangle are the intersection of perpendicular bisectors of any two sides of the triangle.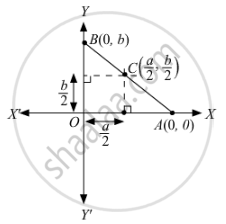
Thus, the coordinates of circumcentre of triangle OAB are \[\left( \frac{a}{2}, \frac{b}{2} \right)\], as shown in the figure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The vertices of a triangle ABC are A (0, 0), B (2, −1) and C (9, 2). Find cos B.
The points A (2, 0), B (9, 1), C (11, 6) and D (4, 4) are the vertices of a quadrilateral ABCD. Determine whether ABCD is a rhombus or not.
The base of an equilateral triangle with side 2a lies along the y-axis, such that the mid-point of the base is at the origin. Find the vertices of the triangle.
Find the distance between P (x1, y1) and Q (x2, y2) when (i) PQ is parallel to the y-axis (ii) PQ is parallel to the x-axis.
A point moves so that the difference of its distances from (ae, 0) and (−ae, 0) is 2a. Prove that the equation to its locus is \[\frac{x^2}{a^2} - \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1\]
Find the locus of a point such that the sum of its distances from (0, 2) and (0, −2) is 6.
Find the locus of a point which moves such that its distance from the origin is three times its distance from the x-axis.
A (5, 3), B (3, −2) are two fixed points; find the equation to the locus of a point P which moves so that the area of the triangle PAB is 9 units.
If A (−1, 1) and B (2, 3) are two fixed points, find the locus of a point P, so that the area of ∆PAB = 8 sq. units.
If O is the origin and Q is a variable point on y2 = x, find the locus of the mid-point of OQ.
What does the equation (x − a)2 + (y − b)2 = r2 become when the axes are transferred to parallel axes through the point (a − c, b)?
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 + xy − 3x − y + 2 = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 − y2 − 2x +2y = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 + xy − 3y2 − y + 2 = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
xy − y2 − x + y = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
xy − x − y + 1 = 0
Find what the following equation become when the origin is shifted to the point (1, 1).
x2 − y2 − 2x + 2y = 0
Find the point to which the origin should be shifted after a translation of axes so that the following equation will have no first degree terms: y2 + x2 − 4x − 8y + 3 = 0
Find the point to which the origin should be shifted after a translation of axes so that the following equation will have no first degree terms: x2 − 12x + 4 = 0
In Q.No. 1, write the distance between the circumcentre and orthocentre of ∆OAB.
If the points (a, 0), (at12, 2at1) and (at22, 2at2) are collinear, write the value of t1 t2.
If the coordinates of the sides AB and AC of ∆ABC are (3, 5) and (−3, −3), respectively, then write the length of side BC.
Write the coordinates of the circumcentre of a triangle whose centroid and orthocentre are at (3, 3) and (−3, 5), respectively.
Write the coordinates of the in-centre of the triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (5, 0) and (0, 12).
If the points (1, −1), (2, −1) and (4, −3) are the mid-points of the sides of a triangle, then write the coordinates of its centroid.
