Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three charges are arranged on the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure. Find the dipole moment of the combination.
उत्तर
The system can be considered as a combination of two dipoles making an angle of 60∘ with each other.
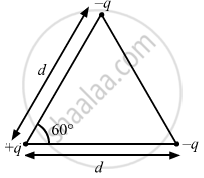
Length of each dipole = d
So, the dipole moment, P = q × d
So, the resultant dipole moment,
\[P_{net} = \sqrt{P^2 + P^2 + 2P\cos60^\circ}\]
\[ = \sqrt{(qd )^2 + (qd )^2 + 2 \left( qd \right)^2 \cos60^\circ}\]
\[ = [ d^2 q^2 + d^2 q^2 + 2 q^2 d^2 \times \frac{1}{2} ]^{1/2} \]
\[ = [3 q^2 d^2 ]^{1/2} = \sqrt{3}qd\]
The net dipole moment is along the bisector of the angle at +q, away from the triangle.
Notes
Figure is missing in the question .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electric dipole of length 4 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of `4sqrt3`Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has charge ±8 nC
A short electric dipole (which consists of two point charges, +q and -q) is placed at the centre 0 and inside a large cube (ABCDEFGH) of length L, as shown in Figure 1. The electric flux, emanating through the cube is:
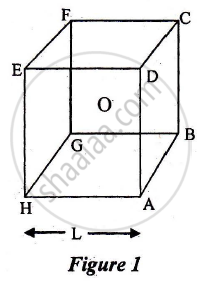
a) `q"/"4piin_9L`
b) zero
c) `q"/"2piin_0L`
d) `q"/"3piin_0L`
(a) Define torque acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in a uniform electric field \[\vec{E}\] Express it in the vector from and point out the direction along which it acts.
(c) What would happen if the external field
Write the expression for the torque \[\vec{\tau}\] acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in an electric field \[\vec{E}\].
An electric dipole of length 2 cm, when placed with its axis making an angle of 60° with a uniform electric field, experiences a torque of \[8\sqrt{3}\] Nm. Calculate the potential energy of the dipole, if it has a charge \[\pm\] 4 nC.
It is said that the separation between the two charges forming an electric dipole should be small. In comparison to what should this separation be small?
An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a sphere. Mark the correct options.
(a) The flux of the electric field through the sphere is zero.
(b) The electric field is zero at every point of the sphere.
(c) The electric field is not zero anywhere on the sphere.
(d) The electric field is zero on a circle on the sphere.
A sample of HCI gas is placed in an electric field of 2.5 × 104 NC−1. The dipole moment of each HCI molecule is 3.4 × 10−30 Cm. Find the maximum torque that can act on a molecule.
Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm. Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm.
Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm. Calculate the electric field at a point on the axis of the dipole 1.0 cm away from the centre.
Two-point charges Q1 = 400 μC and Q2 = 100 μC are kept fixed, 60 cm apart in a vacuum. Find the intensity of the electric field at the midpoint of the line joining Q1 and Q2.
An electric dipole consists of two opposite charges each 0.05 µC separated by 30 mm. The dipole is placed in an unifom1 external electric field of 106 NC-1. The maximum torque exerted by the field on the dipole is ______
Dimensions of mass in electric field and in electric dipole moment are respectively.
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° to a non-uniform electric field. The dipole will experience ________.
The unit of electric dipole moment is ______.
An electric dipole of moment `vec"p"` is placed normal to the lines of force of electric intensity `vec"E"`, then the work done in deflecting it through an angle of 180° is:
In a non-uniform electric field, electric dipole experiences:-
Polar molecules are the molecules ______.
The electric potential V as a function of distance X is shown in the figure.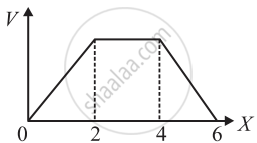
The graph of the magnitude of electric field intensity E as a function of X is ______.
A square surface of side l (m) in the plane of the paper. A uniform electric field E(V/m) also in the plane of the paper is limited only to the lower half of the square surface, the electric flux (in SI units) associated with the surface is ______.