Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two coins are tossed once. Find the probability of getting
1) 2 heads
2) at least 1 tail.
उत्तर
When two coins are tossed, the sample space, S = {(H, H), (H, T), (T, H), (T, T)}
Thus, the total number of outcomes = 4
1) Let A be the event of getting 2 heads.
Thus, outcome favouring A is {(H, H)}
`∴ P(A) = 1/4`
2) Let B be the event of getting at least 1 tail
At least 1 tail means 1 tail or 2 tails.
The outcomes favouring B is {(H, T), (T, H), (T, T)}
`∴ P(B) = 3/4`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Cards bearing numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 and 20 are kept in a bag. A card is drawn at random from the bag. Find the probability of getting a card which is:
1) a prime number
2) a number divisible by 4.
3) a number that is a multiple of 6.
4) an odd number.
A die has 6 faces marked by the given numbers, as shown below.
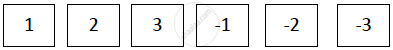
The die is thrown once. What is the probability of getting
1) a positive integer
2) an integer greater than −3.
3) the smallest integer.
Cards marked with numbers 1, 2, 3, 4… 20 are well shuffled and a card is drawn at random. What is the probability that the number on the card is:
(1) A prime number,
(2) A number divisible by 3,
(3) A perfect square?
In a race between Mahesh and John, the probability that John will lose the race is 0.54. Find the probability of:
- winning of Mahesh
- winning of John
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
– 0.6
A ball is drawn at random from a box containing 12 white, 16 red and 20 green balls. Determine the probability that the ball drawn is white.
In a match between A and B; the probability of losing the match is 0.49 for B. What is the probability of winning of A?
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting the jack or the queen of the hearts.
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a diamond.
The heights of 60 students of a class are given in the following table :
| Height(in cm) | 150-155 | 155-158 | 158-160 | 160-165 | 165-172 |
| No. of students | 8 | 20 | 25 | 4 | 3 |
Find the probability that the height of a student lies in the interval
(ii) 150-160
