Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using graph paper and taking 1 cm = 1 unit along both x-axis and y-axis.
1) Plot the points A(–4, 4) and B(2, 2).
2) Reflect A and B in the origin to get the images A’ and B’ respectively.
3) Write down the coordinates of A’ and B’.
4) Give the geometrical name for the figure ABA’B’.
5) Draw and name its lines of symmetry.
उत्तर
Taking 1 cm = 1 unit on graph paper, the points are plotted as below:
(1) and (2)

(3) The image of A' = (4, –4) and B' = (–2, –2)
(4) Now, AB, A'B, AB' and A'B' are equal in length. So, ABA'B' is a rhombus.
(5) The lines of symmetry are the diagonals of the rhombus ABA'B', i.e. AA' and BB'.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use graph paper for this question) (4)
A(0, 3), B(3, −2) and O(0, 0) are the vertices of triangle ABO.
(1) Plot the triangle on a graph sheet taking 2 cm = 1 unit on both the axes.1
(2) Plot D the reflection of B in the Y-axis, and write its coordinates.
(3) Give the geometrical name of the figure ABOD.
(4) Write the equation of the line of symmetry of the figure ABOD.
Complete the following figure, about the given lines of symmetry which are shown by dotted lines and name the figure thus obtained:

Part of a geometrical figure is given in each of the diagram below. Complete the figures so that both the X-axis and the Y-axis are lines of symmetry of the completed figure.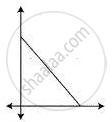
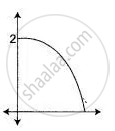
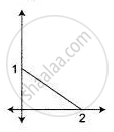

Give the geometrical name of the completed figure.
(You may use graph paper if required).
Freehand sketches would be sufficient.
Which of the following is a symmetrical figure?
Which of the following letters does not have the vertical line of symmetry?
The number of lines of symmetry in a protractor is ______.
The instrument in the geometry box having the shape of a triangle is called a ______.
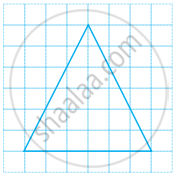
Copy the triangle in the following figure on squared paper. Draw the line(s) of symmetry, if any and identify the type of triangle. (Some of you may like to trace the figure and try paper-folding first!)
On a squared paper, sketch the following:
A quadrilateral with a horizontal line of symmetry but no vertical line of symmetry.
Consider the letters of English alphabets, A to Z. List among them the letters which have horizontal lines of symmetry (like B).
