Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
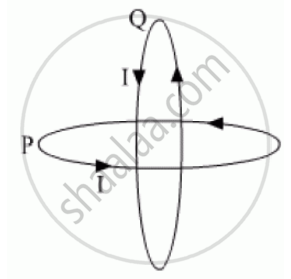
Two identical coils P and Q each of radius R are lying in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils, if they carry currents equal to I and \[\sqrt{3}\] I respectively.

उत्तर
Magnetic field at the centre of the coils due to coil P, having current I is

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
Consider a long, straight wire of cross-sectional area A carrying a current i. Let there be n free electrons per unit volume. An observer places himself on a trolley moving in the direction opposite to the current with a speed \[v = \frac{i}{\text{nAe}}\] and separation from the wire by a distance r. The magnetic field seen by the observer is very nearly
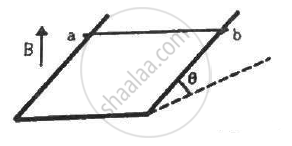
A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth, thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exists in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, show that \[B = \sqrt{\frac{mg R sin\theta}{v l^2 \cos^2 \theta}}\]
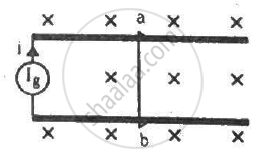
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. Find the velocity of the wire as a function of time.
-
The presence of a large magnetic flux through a coil maintains a current in the coil if the circuit is continuous.
-
A coil of a metal wire kept stationary in a non– uniform magnetic field has an e.m.f induced in it.
-
A charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field at an angle of 85° to the magnetic lines of force, the path of the particle is a circle.
-
There is no change in the energy of a charged particle moving in a magnetic field although a magnetic force is acting on it.
If an electron is moving with velocity `vecnu` produces a magnetic field `vec"B"`, then ______.
A moving charge will gain kinetic energy due to the application of ______.
A beam of protons with speed 4 × 105 ms-1 enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.3 T at an angle of 60° to the magnetic field. The pitch of the resulting helical path of protons is close to :
(Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg, charge of the proton = 1.69 × 10-19 C)
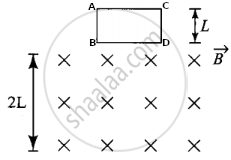
A square coil ABCD with its plane vertical is released from rest in a horizontal uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` of length 2L. The acceleration of the coil is ______.
A charge Q is moving `vec"dl"` distance in the magnetic field `vec"B"`. Find the value of work done by `vec"B"`.
