Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
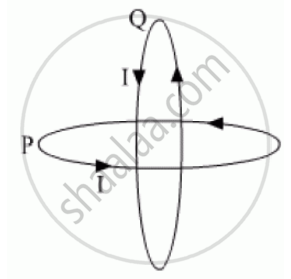
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
उत्तर
Magnetic field at centre of circular loop carrying current I given
`B =(mu_0 I)/(2a)`
Here, a = R
Now, magnetic field due to loop Q
`B_Q = B_x = (mu_0I)/(2R)`
Magnetic field due to loop P.
`B_p = B_y = (mu_0I)/(2R)`
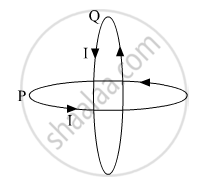
Net field at centre.
`B_N = sqrt(B_p^2 + B_Q^2)`
`= sqrt(((mu_0I)/(2R))^2 +sqrt(((mu_0I)/(2R))^2`
`(mu_0I)/(2R)sqrt2`
`B_N (mu_0I)/(sqrt2R)`
Direction of net magnetic field
tan`theta = B_p/B_Q =1`
`theta =pi/4`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the condition under which the charged particles moving with different speeds in the presence of electric and magnetic field vectors can be used to select charged particles of a particular speed.
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of a diamagnetic material?
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
The motion of copper plate is damped when it is allowed to oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. What is the cause of this damping?
Two proton beams going in the same direction repel each other whereas two wires carrying currents in the same direction attract each other. Explain.
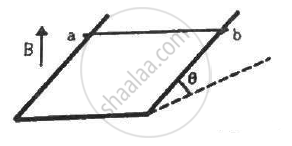
A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth, thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exists in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, show that \[B = \sqrt{\frac{mg R sin\theta}{v l^2 \cos^2 \theta}}\]
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are made to slide on the rails with the same speed 5 cm s−1. Suppose the 19 Ω resistor is disconnected. Find the current through P2Q2 if (a) both the wires move towards right and (b) if P1Q1 moves towards left but P2Q2 moves towards right.

A magnetic field that varies in magnitude from point to point but has a constant direction (east to west) is set up in a chamber. A charged particle enters the chamber and travels undeflected along a straight path with constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle?
Assertion(A): A proton and an electron, with same momenta, enter in a magnetic field in a direction at right angles to the lines of the force. The radius of the paths followed by them will be same.
Reason (R): Electron has less mass than the proton.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity 1 m/s through a perpendicular magnetic field of 1 wb/m2, as shown in figure. If all the four sides are 1 m length each, then the induced emf between A and Din approx is ______V.

