Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The motion of copper plate is damped when it is allowed to oscillate between the two poles of a magnet. What is the cause of this damping?
उत्तर
As the copper plates oscillate in the magnetic field between the two poles of the magnet, there is a continuous change of magnetic field flux linked with the plate. Due to this, eddy currents are set up in the copper plate which try to oppose the motion of the plate according to the Lenz’s law and finally bring it to rest.
संबंधित प्रश्न
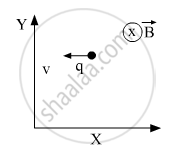
If an electric field \[\vec{E}\] is also applied such that the particle continues moving along the original straight line path, what should be the magnitude and direction of the electric field \[\vec{E}\] ?
A moving charge produces
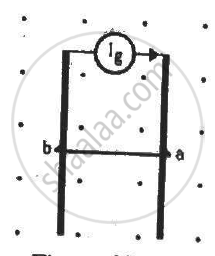
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. The system is kept vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field B that is perpendicular to the plane of the rails (figure). It is found that the wire stays in equilibrium. If the wire ab is replaced by another wire of double its mass, how long will it take in falling through a distance equal to its length?
A deuteron and an alpha particle having equal kinetic energy enter perpendicular into a magnetic field. Let `r_d` and `r_alpha` be their respective radii of the circular path. The value of `(r_d)/(r_alpha)` is equal to ______.
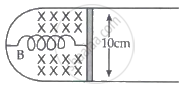
A thin strip 10 cm long is on a U-shaped wire of negligible resistance and it is connected to a spring of spring constant 0.5 Nm-1. The assembly is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.1 T. If the strip is pulled from its equilibrium position and released, the number of oscillations it performs before its amplitude decreases by a factor of e is N. If the mass of the strip is 50 grams, its resistance is 10 Ω, and air drag is negligible, N will be close to ______.
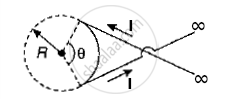
A wire carrying current i has the configuration shown in figure. For the magnetic field to be zero at the centre of the circle, θ must be:
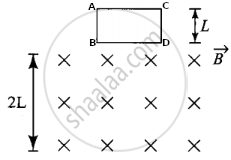
A square coil ABCD with its plane vertical is released from rest in a horizontal uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` of length 2L. The acceleration of the coil is ______.
An α particle is moving along a circle of radius R with a constant angular velocity ω. Point A lies in the same plane at a distance 2R from the centre. Point A records magnetic field produced by α particle, if the minimum time interval between two successive times at which A records zero magnetic field is 't' the angular speed ω, in terms of t is ______.
A charge Q is moving `vec"dl"` distance in the magnetic field `vec"B"`. Find the value of work done by `vec"B"`.
Protons and singly ionized atoms of U235 and U238 are passed in turn (which means one after the other and not at the same time) through a velocity selector and then enter a uniform magnetic field. The protons describe semicircles of radius 10 mm. The separation between the ions of U235 and U238 after describing the semicircle is given by ______.
