Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
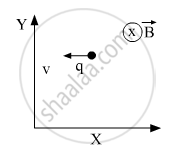
If an electric field \[\vec{E}\] is also applied such that the particle continues moving along the original straight line path, what should be the magnitude and direction of the electric field \[\vec{E}\] ?
उत्तर
The direction of the magnetic force is along negative Y-axis and so, the direction of electric force should be along the positive Y-axis to counter balance the magnetic force and charge particle will move in the straight line path.
Therefore, the direction of electric field is along the positive Y-axis and its magnitude is given by E = vB
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
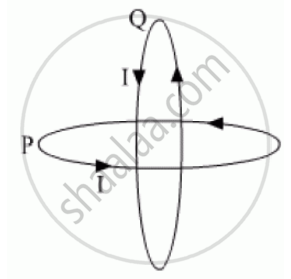
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
Two proton beams going in the same direction repel each other whereas two wires carrying currents in the same direction attract each other. Explain.
A moving charge produces
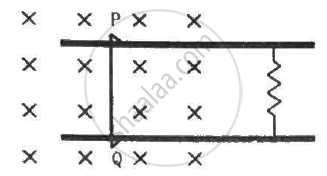
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has mass m, resistance r and can slide on the smooth, horizontal parallel rails separated by a distance l. The resistance of the rails is negligible. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the rectangular region and a resistance R connects the rails outside the field region. At t = 0, the wire PQ is pushed towards right with a speed v0. Find (a) the current in the loop at an instant when the speed of the wire PQ is v, (b) the acceleration of the wire at this instant, (c) the velocity vas a functions of x and (d) the maximum distance the wire will move.
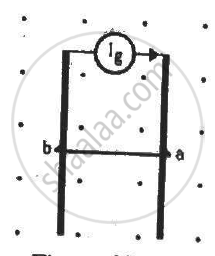
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. The system is kept vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field B that is perpendicular to the plane of the rails (figure). It is found that the wire stays in equilibrium. If the wire ab is replaced by another wire of double its mass, how long will it take in falling through a distance equal to its length?
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then ______.
-
The presence of a large magnetic flux through a coil maintains a current in the coil if the circuit is continuous.
-
A coil of a metal wire kept stationary in a non– uniform magnetic field has an e.m.f induced in it.
-
A charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field at an angle of 85° to the magnetic lines of force, the path of the particle is a circle.
-
There is no change in the energy of a charged particle moving in a magnetic field although a magnetic force is acting on it.
If an electron is moving with velocity `vecnu` produces a magnetic field `vec"B"`, then ______.
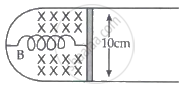
A thin strip 10 cm long is on a U-shaped wire of negligible resistance and it is connected to a spring of spring constant 0.5 Nm-1. The assembly is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.1 T. If the strip is pulled from its equilibrium position and released, the number of oscillations it performs before its amplitude decreases by a factor of e is N. If the mass of the strip is 50 grams, its resistance is 10 Ω, and air drag is negligible, N will be close to ______.