Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. The system is kept vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field B that is perpendicular to the plane of the rails (figure). It is found that the wire stays in equilibrium. If the wire ab is replaced by another wire of double its mass, how long will it take in falling through a distance equal to its length?
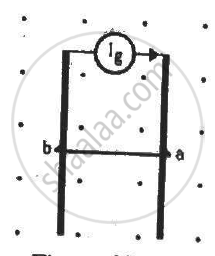
उत्तर
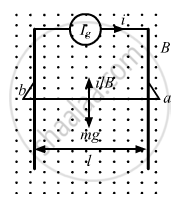
Let us consider the above free body diagram.
As the net force on the wire is zero, ilB = mg.
When the wire is replaced by a wire of double mass, we have
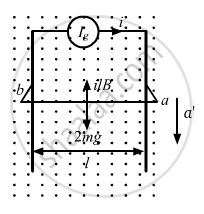
Now, let a' be the acceleration of the wire in downward direction and t be the time taken by the wire to fall.
Net force on the wire = 2mg − ilB = Fnet
On applying Newton's second law, we get
2mg − ilB = 2 ma' ...........(1)
\[\Rightarrow a' = \frac{2mg - ilB}{2 m}\]
\[s = ut + \frac{1}{2}a' t^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow l = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{2mg - ilB}{2m} \times t^2 .............\left[ \because s = l\right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt{\frac{4 ml}{2mg - ilB}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt{\frac{4 ml}{2mg - mg}} .........\text{[From (1)]}\]
` t = 2sqrt(l/g)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the condition under which the charged particles moving with different speeds in the presence of electric and magnetic field vectors can be used to select charged particles of a particular speed.
Depict the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the presence of a diamagnetic material?
If an electric field \[\vec{E}\] is also applied such that the particle continues moving along the original straight line path, what should be the magnitude and direction of the electric field \[\vec{E}\] ?
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting oscillating electric and magnetic fields of an em wave propagating along + z-direction ?
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
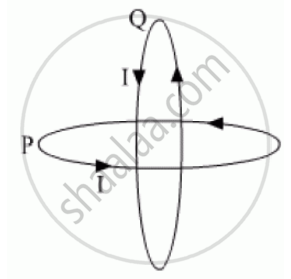
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
Consider a long, straight wire of cross-sectional area A carrying a current i. Let there be n free electrons per unit volume. An observer places himself on a trolley moving in the direction opposite to the current with a speed \[v = \frac{i}{\text{nAe}}\] and separation from the wire by a distance r. The magnetic field seen by the observer is very nearly
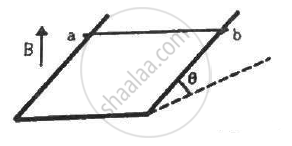
A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth, thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exists in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, show that \[B = \sqrt{\frac{mg R sin\theta}{v l^2 \cos^2 \theta}}\]
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are made to slide on the rails with the same speed 5 cm s−1. Suppose the 19 Ω resistor is disconnected. Find the current through P2Q2 if (a) both the wires move towards right and (b) if P1Q1 moves towards left but P2Q2 moves towards right.

A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then ______.
A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a resultant force ______
A deuteron and an alpha particle having equal kinetic energy enter perpendicular into a magnetic field. Let `r_d` and `r_alpha` be their respective radii of the circular path. The value of `(r_d)/(r_alpha)` is equal to ______.
A beam of protons with speed 4 × 105 ms-1 enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.3 T at an angle of 60° to the magnetic field. The pitch of the resulting helical path of protons is close to :
(Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10-27 kg, charge of the proton = 1.69 × 10-19 C)
A circular coil of radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 3.0 × 10-5 T with its plane perpendicular to the field initially. It is rotated at constant angular speed about an axis along the diameter of coil and perpendicular to magnetic field so that it undergoes half of rotation in 0.2 s. The maximum value of EMF induced (in µV) in the coil will be close to the integer ______.
A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity 1 m/s through a perpendicular magnetic field of 1 wb/m2, as shown in figure. If all the four sides are 1 m length each, then the induced emf between A and Din approx is ______V.

A charged particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 12 kV and acquires a speed of 106 ms-1. It is projected perpendicularly into the magnetic field of strength 0.2 T. The radius of the circle described is ______ cm.
Protons and singly ionized atoms of U235 and U238 are passed in turn (which means one after the other and not at the same time) through a velocity selector and then enter a uniform magnetic field. The protons describe semicircles of radius 10 mm. The separation between the ions of U235 and U238 after describing the semicircle is given by ______.
