Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two resistors of 2.0 Ω and 3.0 Ω are connected (a) in series (b) in parallel, with a battery of 6.0 V and negligible internal resistance. For each case draw a circuit diagram and calculate the current through the battery.
उत्तर
(a) In Series -
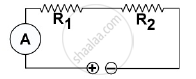
R1 = 2 Ω
R2 = 3 Ω
R = R1 + R2 = 2 + 3 = 5 Ω
V = 6 V
`"I" = "V"/"R"`
I `= 6/5`
I = 1.2 A
(b) In Parallel -
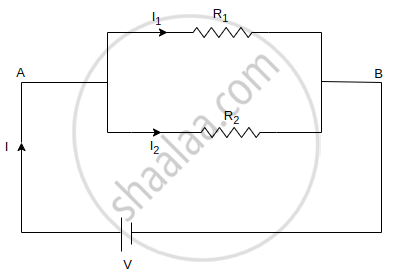
R1 and R2 are connected in parallel
`1/"R" = 1/"R"_1 + 1/"R"_2`
`1/"R" = 1/2+1/3`
`1/"R" = 5/6`
R = `6/5` = 1.2 Ω
V = 6V
I `= "V"/"R"`
`= 6/1.2`
= 5 A
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the current in a circuit if the charge passing each point is 20 C in 40 s?
Fill in the folloing blank with suitable words:
A current is a flow of ............... .For this to happen there must be a ............... circuit.
Which effect of current is utilised in an electric light bulb?
Find the potential difference required to pass a current of 0.2 A in a wire of resistance 20Ω
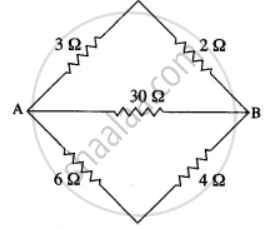
Calculate the equivalent resistance between A and B in the adjacent diagram.
State the relation between work, charge and potential difference for an electric circuit.
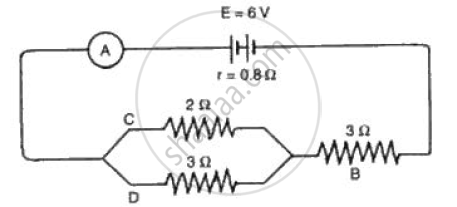
The circuit diagram (Fig.) shows a battery of e.m.f. 6 volts and internal
resistance of 0.8 Ω oonnected in series. Find the
(a) Current reoorded by the ammeter,
(b) P.d. across the terminals of the resistor B,
( c) Current passing through each of the resistors B, C and D, and
( d) P.d. across the terminals of the battery.
Answer the following question.
What is the function of a galvanometer in a circuit?
An electric bulb is marked 100 W, 250 V. How much current will the bulb draw if connected to a 250 V supply?
