Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What can be inferred from the magnetic moment value of the following complex species?
| Example | Magnetic Moment (BM) |
| K2[MnCl4] | 5.9 |
उत्तर
Magnetic Moment (μ) = `sqrt("n"("n" + 2))` BM
When n = 1, μ = `sqrt(1(1 + 2))` = 1.73 BM ≈ 2
When n = 2, μ = `sqrt(2(2 + 2)` = 2.83 BM ≈ 3
When n = 3, μ = `sqrt(3(3 + 2))` = 3.87 BM ≈ 4
When n = 4, μ = `sqrt(4(4 + 2))` = 4.90 BM ≈ 5
When n = 5, μ = `sqrt(5(5 + 2))` = 5.92 BM ≈ 6
K2[MnCl4]: μ = 5.9 BM, Mn2+ ion has 5 unpaired electrons. Its orbital diagram is:
| 3d | ||||
| ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following cations are coloured in aqueous solutions and why ?
Sc3+, V3+, Ti4+, Mn2+ (At. Nos. Sc = 21, V = 23, Ti = 22, Mn = 25)
The elements of 3d transition series are given as: Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co
Answer the following: Which element is a strong oxidising agent in +3 oxidation state and why?
Write down the number of 3d electrons in the following ion:
Cu2+
Indicate how would you expect the five 3d orbitals to be occupied for this hydrated ions (octahedral).
NF3 is possible, but NF5 is not. Why?
Write balanced chemical equations for the conversion of `CrO_4^(2-)` to `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` in acidic medium and `Cr_2O_7^(2-)` to `CrO_4^(2-)`
in basic medium.
Explain why transition elements form alloys.
Transition elements show magnetic moment due to spin and orbital motion of electrons. Which of the following metallic ions have almost same spin only magnetic moment?
(i) \[\ce{Co^{2+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Cr^{2+}}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Mn^{2+}}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Cr^{3+}}\]
Although fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen, but the ability of oxygen to stabilise higher oxidation states exceeds that of fluorine. Why?
Although \[\ce{Cr^3+}\] and \[\ce{Co^2+}\] ions have same number of unpaired electrons but the magnetic moment of \[\ce{Cr^3+}\] is 3.87 B.M. and that of \[\ce{Co^2+}\] is 4.87 B.M. Why?
Assertion: Separation of \[\ce{Zr}\] and \[\ce{Hf}\] is difficult.
Reason: Because \[\ce{Zr}\] and \[\ce{Hf}\] lie in the same group of the periodic table.
Mention any three processes where transition metals act as catalysts.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
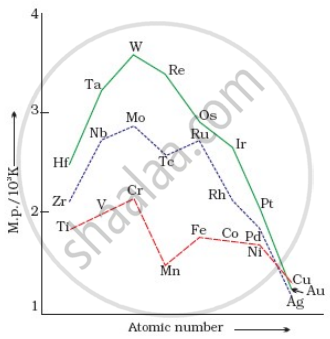
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Which of the following species has maximum magnetic momentum?
The basic character of transition metals monoxide follow the order.
A transition element X has an electronic configuration [Ar]4s23d3. Predict its likely oxidation states.
Explain the use of different transition metals as catalysts.
Account for the following:
Zirconium (Zr) and Hafnium (Hf) are difficult to separate.
A coordination compound has the formula \[\ce{CoCl3.4NH3}\]. It precipitates silver ions as AgCl and its molar conductance corresponds to a total of two ions.
Based on this information, answer the following question:
- Deduce the structural formula of the complex compound.
- Write the IUPAC name of the complex compound.
- Draw the geometrical isomers of the complex compound.
Decide which of the following atomic numbers are the atomic numbers of the inner transition elements:
29, 59, 74, 95, 102, 104
