Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the gravitational force between two objects when the distance between them is :
(1) doubled ?
(2) halved ?
उत्तर
`F = (GMm)/r^2`
where,
F − gravitational force
G − gravitational constant
M − mass of the earth
m − mass of object
r − distance
(i). r = doubled
`F = (GMm)/r^2` keeping everything constant i.e. G, M, m
= `(GMm)/(2r)^2`
= `(GMm)/(4r^2)`
F becomes one-fourth.
(ii) r = halved
`F = (GMm)/r^2` keeping everything constant i.e. G, M, m
= `(GMm)/(1/(2r))^2`
= `(GMm)/(1/(4r))^2`
= `(4GM m)/(r^2)`
F becomes four times the original.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the scientist who gave the three laws of planetary motion.
What type of force is involved in the formation of tides in the sea ?
What is the actual shape of the orbit of a planet around the sun? What assumption was made by Newton regarding the shape of an orbit of a planet around the sun of deriving his inverse square rule from Kepler's third law of planetary motion?
The masses of the earth and moon are 6 × 1024 kg and 7.4 × 1022 kg, respectively. The distance between them is 3.8 × 105 km. Calculate the gravitational force of attraction between the two?
Use G = 6.7 × 10–11 N m2 kg–2
Write proper answer in the box:
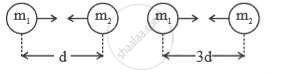
If `"F" = ("G""m"_1"m"_2)/"d"^2` then F = ______
In the relation F = G ✕ M ✕ m/d2, the quantity G:
A _______ is necessary to change the speed as well as the direction of motion of an object.
The atmosphere is held to the earth by
An apple falls from a tree because of gravitational attraction between the earth and the apple. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the earth on the apple and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the apple on earth, then
Identical packets are dropped from two aeroplanes, one above the equator and the other above the north pole, both at height h. Assuming all conditions are identical, will those packets take some time to reach the surface of the earth. Justify your answer.
