Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens when a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol.
उत्तर
- When a beam of light is passed through colloidal sol, it is observed that the colloidal particles scatter some of the incident light in all directions.
- Because of this scattering of light, the path of light through the colloidal dispersion becomes visible to an observer standing at right angles to its path, and the phenomenon is known as the Tyndall effect.
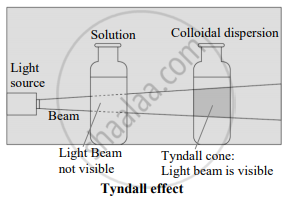
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write one difference in Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
Define the following with a suitable example, of each:
Multimolecular colloid
Define the following with a suitable example, of each:
Gel
Write Hardy-Sulze rules.
Which type of colloid is formed on the dissolution of soap in water?
Froth and whipped cream are examples of ____________.
Identify the CORRECT statement.
In coagulation of positively charged ferric hydroxide sol, the most and least effective ions are ____________ and ____________ respectively.
Which of the following is a heterogeneous mixture?
The order of coagulating power of following ions in the coagulation of a positive sol is:
i. \[\ce{PO^{3-}_4}\]
ii. \[\ce{SO^{2-}_4}\]
iii. \[\ce{[Fe(CN)6]^{4-}}\]
iv. \[\ce{NO^-_3}\]
Maximum coagulation power is in ____________.
Which of the following is NOT true for lyophilic colloids?
Tyndall effect is observed due to ____________.
Smoke is an example of ____________.
Froth is a colloidal solution of ____________.
In which of the following sols there is low affinity between dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
Some colloids are stable by their nature, i.e., gels, alloys, and solid foams. Gelatin and jellies are two common examples of a gel. The solid and liquid phases in a gel are interdispersed with both phases being continuous. In most systems, the major factor influencing the stability is the charge on the colloidal particles. If a particular ion is preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the particles, the particles in suspension will repel each other, thereby preventing the formation of aggregates that are larger than colloidal dimensions. The ion can be either positive or negative depending on the particular colloidal system, i.e., air bubbles accumulate negative ions, sulphur particles have a net negative charge in a sulphur sol, and the particles in a metal hydroxide sol are positively charged. Accumulation of charge on a surface is not an unusual phenomenon-dust is attracted to furniture surfaces by electrostatic forces. When salts are added to lyophobic colloidal systems the colloidal particles begin to form larger aggregates and a sediment forms as they settle. This phenomenon is called flocculation, and the suspension can be referred to as flocculated, or colloidally unstable. If the salt is removed, the suspension can usually be restored to its original state; this process is called deflocculation or peptization. The original and restored colloidal systems are called deflocculated, peptized, or stable sols.
Why does a small amount of salt have such a dramatic effect on the stability of a lyophobic colloidal system? The answer lies in an understanding of the attractive and repulsive forces that exist between colloidal particles. Van der Waals forces are responsible for the attractions, while the repulsive forces are due to the surface charge on the particles. In a stable colloid, the repulsive forces are of greater magnitude than the attractive forces. The magnitude of the electrical repulsion is diminished by addition of ionized salt, which allows the dispersed particles to aggregate and flocculate. River deltas provide an example of this behaviour. A delta is formed at the mouth of a river because the colloidal clay particles are flocculated when the freshwater mixes with the salt water of the ocean.
Gelatin is a _________ colloidal system.
Some colloids are stable by their nature, i.e., gels, alloys, and solid foams. Gelatin and jellies are two common examples of a gel. The solid and liquid phases in a gel are interdispersed with both phases being continuous. In most systems, the major factor influencing the stability is the charge on the colloidal particles. If a particular ion is preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the particles, the particles in suspension will repel each other, thereby preventing the formation of aggregates that are larger than colloidal dimensions. The ion can be either positive or negative depending on the particular colloidal system, i.e., air bubbles accumulate negative ions, sulphur particles have a net negative charge in a sulphur sol, and the particles in a metal hydroxide sol are positively charged. Accumulation of charge on a surface is not an unusual phenomenon-dust is attracted to furniture surfaces by electrostatic forces. When salts are added to lyophobic colloidal systems the colloidal particles begin to form larger aggregates and a sediment forms as they settle. This phenomenon is called flocculation, and the suspension can be referred to as flocculated, or colloidally unstable. If the salt is removed, the suspension can usually be restored to its original state; this process is called deflocculation or peptization. The original and restored colloidal systems are called deflocculated, peptized, or stable sols.
Why does a small amount of salt have such a dramatic effect on the stability of a lyophobic colloidal system? The answer lies in an understanding of the attractive and repulsive forces that exist between colloidal particles. Van der Waals forces are responsible for the attractions, while the repulsive forces are due to the surface charge on the particles. In a stable colloid, the repulsive forces are of greater magnitude than the attractive forces. The magnitude of the electrical repulsion is diminished by addition of ionized salt, which allows the dispersed particles to aggregate and flocculate. River deltas provide an example of this behaviour. A delta is formed at the mouth of a river because the colloidal clay particles are flocculated when the freshwater mixes with the salt water of the ocean.
Colloidal solutions are stable due to ______.
Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by ______.
A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as ______.
Which of the following process is responsible for the formation of delta at a place where rivers meet the sea?
An emulsion cannot be broken by:
(i) heating
(ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium
(iii) freezing
(iv) adding emulsifying agent
Gelatin which is a peptide is added in icecreams. What can be its role?
A colloid is formed by adding \[\ce{FeCl3}\] in excess of hot water. What will happen if excess sodium chloride is added to this colloid?
Why does bleeding stop by rubbing moist alum?
Which of the following substances will precipitate the negatively charge emulsion
The size of a raw mango shrinks to a much smaller size when kept in a concentrated salt solution. Which one of the following processes can explain this?
In which of the following, the Tyndall effect is not observed?
Smoke is an example of ______.
