Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone?
उत्तर
The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a low-pressure zone located at the equator where trade winds converge, and so, it is a zone where air tends to ascend. In July, the ITCZ has located around 20° N-25° N latitudes (over the Gangetic plain). These are sometimes called the monsoon trough. This monsoon trough encourages the development of thermal low over north and northwest India. Due to the shift of ITCZ, the trade winds of the southern hemisphere cross the equator between 40° and 60° E longitudes and start blowing from southwest to northeast due to the Coriolis force. It becomes southwest monsoon. In winter, the ITCZ moves southward, and so the reversal of winds from northeast to south and southwest takes place. They are called northeast monsoons.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name two types of cyclonic systems that affect India and two areas that receive rainfall from these systems.
Give two important characteristics of the South West monsoon rainfall.
State the main factors that affect the climate of Indian sub-continent.
At a place like Bhopal one can see the midday sun exactly over head twice a year, while at vidisha, only a few kilometre north of it, one is not able to do so even once. Give the reason briefly.
Explain giving any two reasons why the deltas of the river Mahanadi suffer from occasional floods.
Study the temperature and rainfall graph of station X given below and answer the questions that follow :
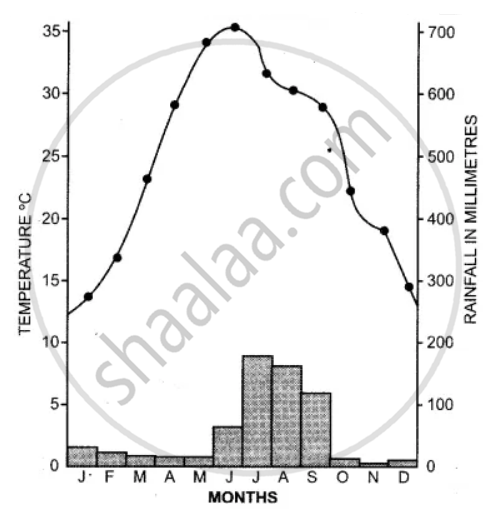
(i) Is the location of station X inland or coastal?
(ii) What is the cause of a sudden fall of temperature in July, even though it is a summer month?
(iii) Mention one main feature of the climate experienced by the station X.
Study the climatic data provided in the table below for a city A in India and answer the questions that follow :
| City | T/R | J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| A | T | -8 | -3 | 2 | 7 | 15 | 18 | 17 | 12 | 10 | 5 | 0 | -7 |
| R | 10 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 13 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
T = Mean monthly temperature in degree Celsius (°C).
R = Average monthly rainfall in millimeters (mm).
(i) What is the cause of low rainfall in station A?
(ii) Calculate the range of temperature of this station.
Study the Temperature-Rainfall graph of station X below and answer the questions that follow :
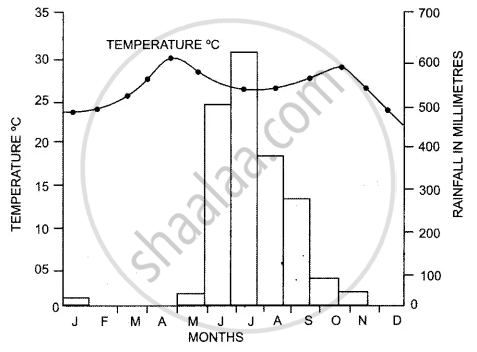
(a) Is the location of station X Inland or coastal ? Give a reason for your answer.
(b) Which branch of the South West Monsoon brings, rain from the month of June to September?
Explain how the following factor affect India’s climate :
Southern Oscillation
Continental climate is experienced by ______.
The unifying factor of the climate of India is ______ winds.
Retreating monsoon winds flow from ______.
The most dominant factor which affects the climate of India is ______.
Consider the given statements and choose the correct option from the given below ones
Assertion(A): The Himalayas acts as a climatic barrier.
Reason(R): The Himalayas prevents cold winds from central Asia and keep the Indian Sub-continent warm.(Give option for this questions)
List the factors aff ecting climate of India.
What is meant by 'normal lapse rate'?
Name the areas which receive heavy rainfall.
Mountains are cooler than the plains.
Retreating monsoon winds flow from ______.
The cold polar winds from Central Asia is prevented by the ______.
Jet streams cause rainfall in ______ India.
Tamil Nadu gets its winter rainfall from the ______ winds.
What is the weather?
Name the factors affecting the climate of India.
Give reasons for the following topic:
The relief of India has a great bearing on the climate.
Find out the temperature of Ooty (2240m) when it is 35°C in Chennai (6.7m)
