Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is wavefront? How is it related to rays of light? What is the shape of the wavefront at a point far away from the source of light?
उत्तर
The locus of all points having the same phase at a given instant of time is called a wavefront.
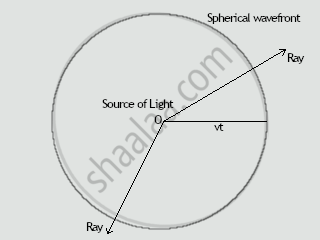
Consider a light source O in a homogeneous isotropic medium with a speed of light of v. Light is emitted from the source in all directions. The disturbance (light energy) from the source covers a distance vt in all directions in time t, i.e., it reaches all points at a distance vt from the point source. The surface of a sphere with centre O and radius vt is the locus of these points in the same phase. Three dimensional waves like the sound waves produced by a source of sound, or light waves produced by a light source, travel in all directions away from the source and propagate in three dimensions. Such a wave is called a spherical wave. The arrows are perpendicular to the spherical surfaces and show the direction of propagation of the waves. These arrows are the rays of light that we have considered in the earlier study of optics. consider a spherical wavefront that has travelled a large distance away from the source. If we take a small portion of this wavefront, it will appear to be a plane surface (just like the surface of the earth around us appears to be flat to us) with the direction of propagation perpendicular to it. In such a case the wave is called a plane wave.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are primary and secondary sources of light?
Derive the laws of reflection of light using Huygens’ principle.
Answer in brief:
Explain what is meant by polarization and derive Malus’ law.
What are Secondary sources? State Huygens’ Principle.
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ is incident on the plane reflecting surface. After reflection, its wavelength will be ______
Wavefront is the locus of all points, where the particles of the medium vibrate with the same ____________.
A plane wavefront is an incident on a water surface at an angle of incidence 60° then it gets refracted at 45°. The ratio of the width of incident wavefront to that of refracted wavefront will be ______
`[sin pi/4 = cos pi/4 = 1/sqrt2, sin60^circ = sqrt3/2, cos60^circ = 1/2]`
In Huygens' wave theory, the locus of all points in the same state of vibration is called ______.
The direction of wavefront of a wave with the wave motion is ______.
Explain the construction and propagation of a spherical wavefront using Huygens's principle.
State laws of reflection.
Wave normals to spherical wavefronts can be ______.
