Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What kind of fringes do you expect to observe if white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
उत्तर
White light consists of waves of all wavelengths starting from violet to red colour. If the monochromatic light in Young’s interference experiment is replaced by white light, then the waves of each wavelength form their separate interference patterns. The resultant effect of all these patterns is obtained on the screen.
The path difference between waves starting from S1 and S2 at the location (M) of central fringe is zero, i.e., for point M of screen S1M − S2M=0 i.e., the waves of all colours reach at midpoint M in the same phase. Therefore the central fringe (at M) is white. As fringe width ω = Dλ/d or ω ∝ α and in visible region wavelength of violet colour is least and that of red colour is maximum, i.e., wavelength increases in the order of colours denoted by VIBGYOR therefore on either side of it some coloured fringes are obtained in order of colour VIBGYOR. That is the violet (V) fringe appears first and the red (R) the last. After this, the fringes of many colours overlap at each point of the screen and so the screen appears uniformly illuminated.
Thus if we use white light in place of monochromatic light the central fringe is white, containing on either side a few coloured fringes (in order VIBGYOR) and the remaining screen appears uniformly illuminated.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2.0 × 10−3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
A monochromatic ray of light falls on a regular prism. What is the relation between the angle of incidence and angle of emergence in the case of minimum deviation?
State Huygen’s principle. Using this principle explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a narrow beam coming from a `=> n = (vlamda)/(vlamda_omega)`monochromatic source of light is incident normally.
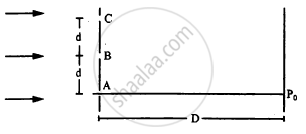
The following figure shows three equidistant slits being illuminated by a monochromatic parallel beam of light. Let \[B P_0 - A P_0 = \lambda/3\text{ and }D > > \lambda.\] (a) Show that in this case \[d = \sqrt{2\lambda D/3}.\] (b) Show that the intensity at P0 is three times the intensity due to any of the three slits individually.
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Answer the following question.
In the diffraction due to a single slit experiment, the aperture of the slit is 3 mm. If monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is incident normally on the slit, calculate the separation between the first order minima and the 3rd order maxima on one side of the screen. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m.
(a) Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
(b) The intensity at the central maximum (O) in Young's double-slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would `"I"_°/4`
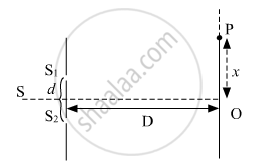
(c) In Young's double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0⋅5 mm and the screen is placed 1⋅0 m away from the slit. It is found that the 5th bright fringe is at a distance of 4⋅13 mm from the 2nd dark fringe. Find the wavelength of light used.
A monochromatic ray of light falls on a regular prism under minimum deviation condition. What is the relation between angle of incidence and angle of emergence?
Assertion(A): The photoelectrons produced by a monochromatic light beam incident on a metal surface have a spread in their kinetic energies.
Reason(R): The energy of electrons emitted from inside the metal surface, is lost in collision with the other atoms in the metal.
