Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the work done by the field of a nucleus in a complete circular orbit of the electron? What if the orbit is elliptical?
उत्तर
Whenever the electron completes an orbit, either circular or elliptical, the work done by the field of a nucleus is zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
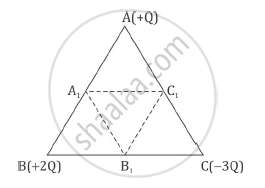
Three point charges, + Q + 2Q and – 3Q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side l. If these charges are displaced to the mid-point A1, B1 and C1, respectively, find the amount of the work done in shifting the charges to the new locations.
In a hydrogen atom, the electron and proton are bound at a distance of about 0.53 Å:
(a) Estimate the potential energy of the system in eV, taking the zero of the potential energy at infinite separation of the electron from proton.
(b) What is the minimum work required to free the electron, given that its kinetic energy in the orbit is half the magnitude of potential energy obtained in (a)?
(c) What are the answers to (a) and (b) above if the zero of potential energy is taken at 1.06 Å separation?
We know that electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a charged conductor. Is electric potential also discontinuous there?
Guess a possible reason why water has a much greater dielectric constant (= 80) than say, mica (= 6).
Three point charges +q each are kept at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 'l'. Determine the magnitude and sign of the charge to be kept at its centroid so that the charges at the vertices remain in equilibrium.
The electrostatic potential energy of two-point charges, 1 µC each, placed 1 meter apart in the air is:
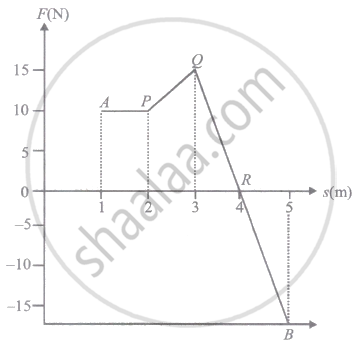
A body moves from point A to B under the action of a force, varying in magnitude as shown in the figure. Force is expressed in newton and displacement in meter. What is the total work done?
If stretch in a spring of force constant k is tripled then the ratio of elastic potential energy in the two cases will be:
A work of 100 joule is performed in carrying a charge of 5 coulomb form infinity to a particular. point in an' electrostatic field. The potential of this point is:-
When one electron is taken towards the other electron, then the electric potential energy of the system ______
In a region of constant potential ______.
- the electric field is uniform
- the electric field is zero
- there can be no charge inside the region
- the electric field shall necessarily change if a charge is placed outside the region
Three-point charges Q, q and -q are kept at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side L as shown in the figure. What is
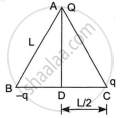
- the electrostatic potential energy of the arrangement? and
- the potential at point D?
