Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following sources provides the best monochromatic light?
विकल्प
A candle
A bulb
A mercury tube
A laser
उत्तर
A laser
Among the given sources, laser is the best coherent source providing monochromatic light with constant phase difference.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2.0 × 10−3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source
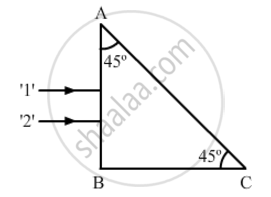
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.3 and 1.5. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
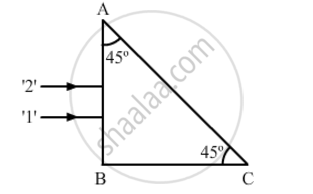
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.35 and 1.45. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
In the wave picture of light, the intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
State the essential conditions for diffraction of light ?
Monochromatic light of frequency 5.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 3.0 × 10–3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source ?
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, why does the refracted light have the same frequency as that of the incident light?
If a monochromatic source of light is replaced by white light, what change would you observe in the diffraction pattern?
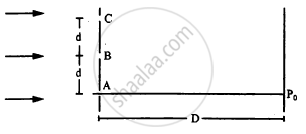
The following figure shows three equidistant slits being illuminated by a monochromatic parallel beam of light. Let \[B P_0 - A P_0 = \lambda/3\text{ and }D > > \lambda.\] (a) Show that in this case \[d = \sqrt{2\lambda D/3}.\] (b) Show that the intensity at P0 is three times the intensity due to any of the three slits individually.
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The two slits S1 and S2 placed symmetrically around the central line are illuminated by a monochromatic light of wavelength λ. The separation between the slits is d. The light transmitted by the slits falls on a screen ∑1placed at a distance D from the slits. The slit S3 is at the central line and the slit S4 is at a distance z from S3. Another screen ∑2 is placed a further distance D away from ∑1.Find the ratio of the maximum to minimum intensity observed on ∑2 if z is equal to
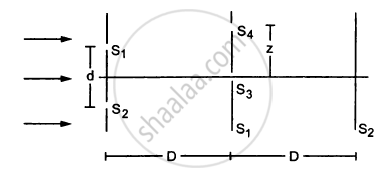
(a) \[z = \frac{\lambda D}{2d}\]
(b) \[\frac{\lambda D}{d}\]
(c) \[\frac{\lambda D}{4d}\]
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 cm and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the . central maxima.
Find the angle of incidence at which a ray of monochromatic light should be incident on the first surface AB of a regular glass prism ABC so that the emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. (Refractive Index of glass = 1 .56)
Answer the following question.
In the diffraction due to a single slit experiment, the aperture of the slit is 3 mm. If monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is incident normally on the slit, calculate the separation between the first order minima and the 3rd order maxima on one side of the screen. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m.
A narrow slit is illuminated by a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ equal to 6000 Å and the angular width of the central maximum in the resulting diffraction pattern is measured. When the slit is next illuminated by light of wavelength λ’, the angular width decreases by 30%. Calculate the value of the wavelength λ’.
