Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The two slits S1 and S2 placed symmetrically around the central line are illuminated by a monochromatic light of wavelength λ. The separation between the slits is d. The light transmitted by the slits falls on a screen ∑1placed at a distance D from the slits. The slit S3 is at the central line and the slit S4 is at a distance z from S3. Another screen ∑2 is placed a further distance D away from ∑1.Find the ratio of the maximum to minimum intensity observed on ∑2 if z is equal to
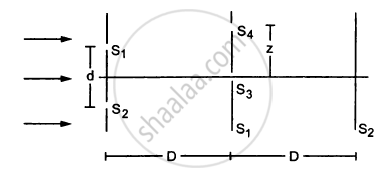
(a) \[z = \frac{\lambda D}{2d}\]
(b) \[\frac{\lambda D}{d}\]
(c) \[\frac{\lambda D}{4d}\]
उत्तर
Given:
Separation between the two slits = d
Wavelength of the light = \[\lambda\]
Distance of the screen = D
The fringe width (β) is given by \[\beta = \frac{\lambda D}{d}\]
At S3, the path difference is zero. So, the maximum intensity occurs at amplitude = 2a.
(a) When \[z = \frac{D\lambda}{2d}\]
The first minima occurs at S4, as shown in figure (a).
With amplitude = 0 on screen ∑2, we get
\[\frac{l_{max}}{l_{min}} = \frac{\left( 2a + 0 \right)^2}{\left( 2a - 0 \right)^2} = 1\]
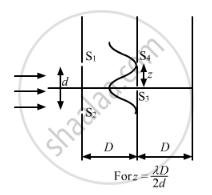
(b) When \[z = \frac{D\lambda}{d}\]
The first maxima occurs at S4, as shown in the figure.
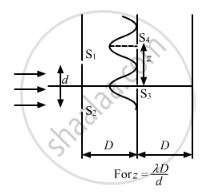
With amplitude = 2a on screen ∑2, we get
\[\frac{l_\max}{l_\min} = \frac{\left( 2a + 2a \right)^2}{\left( 2a - 2a \right)^2} = \infty \]
(c) When \[z = \frac{D\lambda}{4d}\]
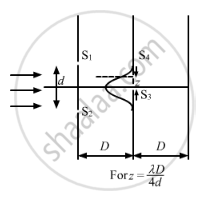
The slit S4 falls at the mid-point of the central maxima and the first minima, as shown in the figure.
Intensity \[= \frac{l_\max}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \text{Amplitude }= \sqrt{2}a\]
\[\therefore \frac{l_\max}{l_\min} = \frac{\left( 2a + \sqrt{2}a \right)^2}{\left( 2a - \sqrt{2}a \right)^2} = 34\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2.0 × 10−3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source
'Two independent monochromatic sources of light cannot produce a sustained interference pattern'. Give reason.
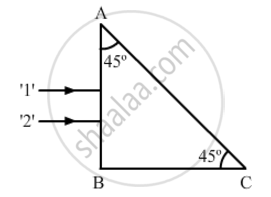
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.35 and 1.45. Trace the path of these rays after entering the prism.
What kind of fringes do you expect to observe if white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
A monochromatic ray of light falls on a regular prism. What is the relation between the angle of incidence and angle of emergence in the case of minimum deviation?
Monochromatic light of frequency 5.0 × 1014 Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 3.0 × 10–3 W. Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source ?
When monochromatic light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, explain the following, giving reasons:
(i) Is the frequency of reflected and refracted light same as the frequency of incident light?
(ii) Does the decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by light wave?
Obtain the conditions for the bright and dark fringes in diffraction pattern due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source.
Explain clearly why the secondary maxima go on becoming weaker with increasing.
Which of the following sources provides the best monochromatic light?
"Monochromatic light should be used to produce pure spectrum". Comment on this statement.
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Monochromatic light of wavelength 650 nm falls normally on a slit of width 1.3 x 10-4 cm and the resulting Fraunhofer diffraction is obtained on a screen. Find the angular width of the . central maxima.
Find the angle of incidence at which a ray of monochromatic light should be incident on the first surface AB of a regular glass prism ABC so that the emergent ray grazes the adjacent surface AC. (Refractive Index of glass = 1 .56)
Monochromatic fight of wavelength 198 nm is incident on the surface of a metallic cathode whose work function is 2.5 eV How much potential difference must be applied between the cathode and the anode of a photocell to just stop the photocurrent from flowing?
Using the monochromatic light of the wavelength in the experimental set-up of the diffraction pattern as well as in the interference pattern where the slit separation is 1 mm, 10 interference fringes are found to be within the central maximum of the diffraction pattern. Determine the width of the single slit, if the screen is kept at the same distance from the slit in the two cases.
Assertion(A): The photoelectrons produced by a monochromatic light beam incident on a metal surface have a spread in their kinetic energies.
Reason(R): The energy of electrons emitted from inside the metal surface, is lost in collision with the other atoms in the metal.
A ray of monochromatic light propagating in the air is incident on the surface of the water. Which of the following will be the same for the reflected and refracted rays?
