Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following are exclusive endocrine glands?
विकल्प
Thymus and testis
Adrenal and ovary
Parathyroid and adrenal
Pancreas and parathyroid
उत्तर
Parathyroid and adrenal
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define Endocrine gland
Give an example of hyperglycemic hormone.
Give an example of a blood pressure lowering hormone.
add a note on deficiency of thyroxine.
In the table given below, fill in the blanks by naming endocrine glands, the hormones they secrete, and the function they perform, in a normal person.
| S.No. | Name of the gland | produced | Function |
| 1. | Thyroid | ||
| 2. | Insulin | ||
| 3. | Preparing the body for action | ||
| 4. | (i) Growth hormone (ii) Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
What is the difference between an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland?
What would a child suffer from if there was hyposecretion from his thyroid?
Compare the hormonal response with the nervous response with respect to their speed, transmission and the general nature of changes brought about.
Given alongside is an outline diagram of human body showing position of certain organs.
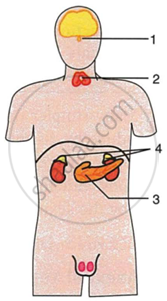 |
- Name the parts numbered 1 to 4.
- What is common to all these parts in regard to the nature of their functions?
- Name the nutrient element which is essential for the normal working of part 2.
The diagram give below represents an endocrine gland in the human body. Study the diagram and answer the following questions: 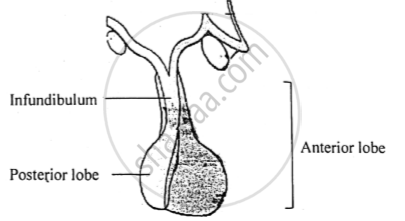
Explain the term ‘Hormone’. What is the role of Tropic hormones in the human body?
Give the special function of the following:
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
Give the special function of the following:
Corpus luteum
Define the following:
Exocrine gland
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Increased reabsorption of water in the kidneys
What are the general properties of hormones?
Name the different endocrine glands found in the body of man.
Complete the following:
| Gland/Organ | Hormone | Function |
| (i) Stomach | __________ | __________ |
| (ii) Parathyroid | __________ | __________ |
| (iii) __________ | __________ | Lowers blood sugar level. |
| (iv) Adrenal medulla | __________ | __________ |
| (v) Pancreas (Alpha cells) | __________ | __________ |
| (vi) Testes | __________ | __________ |
Differentiate: Gigantism and Acromegaly.
Differentiate: Acromegaly and Myxedema.
Name the Following: Hormone controls absorption of water from kidney tubules.
Give the Technical Term: Name a hormone which controls developments of male secondary sexual characters.
Give the Technical Term: The structure which controls the master gland.
Give the Technical Term: Name the glands which secrete the following hormone: Testosterone
Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:
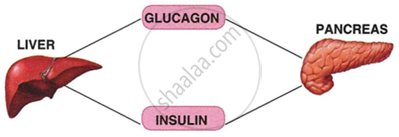 |
- Name the cells of the pancreas that produce (1) glucagon (2) insulin.
- State the main function of (1) glucagon and (2) insulin.
- Why is the pancreas referred to as an exo-endocrine gland?
- Why is insulin not given orally but is injected into the body?
- What is the technical term for the cells of the pancreas that produce endocrine hormones?
- Where in the body is the pancreas located?
State the Location
Prostate gland
State the Function
Oestradiol
State the Function
Progesterone
Choose the Odd One Out
Choose the Odd One Out
Vasopressin is concerned with:
Which organ acts a temporary endocrine gland in females?
Serum calcium level is regulated by ______.
Write the role of oestrogen in ovulation?
Differentiate hyperglycemia from hypoglycemia.
Given below is the figure showing the human urinary system with structures labelled A to D. Select the option which correctly identifies them and gives their function.
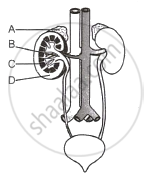
Acromegaly is caused by ______.
Choose the odd one out from series and write the category of the remaining terms:
Distinguish between the following pair:
Enzymes and hormones (mode of transport and target organ)
