Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why are the emitter, the base, and the collector of a BJT doped differently?
उत्तर
A BJT is a bipolar device, both electrons and holes participate in the conduction process. Under the forward-biased condition, the majority of carriers injected from the emitter into the base constitute the largest current component in a BJT. For these carriers to diffuse across the base region with negligible recombination and reach the collector junction, they must overwhelm the majority of carriers of the opposite charge in the base. The total emitter current has two components, due to majority carriers in the emitter and due to minority carriers diffusing from the base into the emitter. The ratio of the current component due to the injected majority carriers from the emitter to the total emitter current is a measure of the emitter efficiency. To improve the emitter efficiency and the common-base current gain (α), it can be shown that the emitter should be much more heavily doped than the base.
Also, the base width is a function of the base-collector voltage. A low doping level of the collector increases the size of the depletion region. This increases the maximum collector-base voltage and reduces the base width. Further, the large depletion region at the collector-base junction-extending mainly into the collector-corresponds to a smaller electric field and avoids avalanche breakdown of the reverse-biased collector-base junction.
[Note: Effective dopant concentrations of (a) npn transistor (b) pnp transistor are shown below.]
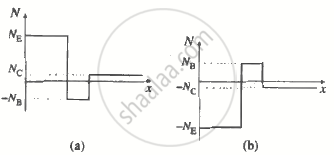
The base doping is less than the emitter doping but greater than the collector doping.
संबंधित प्रश्न
The common-base DC current gain of a transistor is 0.967. If the emitter current is 10mA. What is the value of base current?
Derive the relation between α and β.
Explain the working of the PNP transistor?
Draw the circuit diagram to study the characteristic of the transistor in common emitter mode. Draw the input and output characteristics.
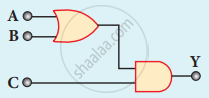
The output of the following circuit is 1 when the input ABC is
Explain the need for a feedback circuit in a transistor oscillator.
What is rectification?
Transistor functions as a switch. Explain.
A transistor having α = 0.8 is connected in common emitter configuration. When the base current changes by 6 mA, then the change in collector current is ______.
Least doped region in a transistor ____________.
In a common emitter amplifier circuit using an n-p-n transistor, the phase difference between the input and the output voltages will be: ____________.
In a transistor, a change of 8.0 mA in the emitter current produces a change of 7.8 mA in the collector current. Then change in the base current is ____________.
A transistor when connected in common emitter mode has a ____________.
The current gain `alpha` of a transistor is 0.95. The change in collector current corresponding to a change of 0.4 mA in the base current in a common emitter arrangement is ______.
In a transistor, the thickness of the base region ____________.
A change of 9.0 mA in the emitter current brings a change of 8.9 mA in the collector current. The value of current gain β will be ______.
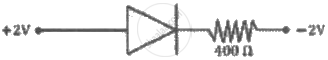
For an ideal diode, the current in the following arrangement is ______.
A transistor having α = 0.8 is connected in a common emitter configuration. When the base current changes by 6 mA, the change in collector current is ______
A conducting wire has length 'L1' and diameter 'd1'. After stretching the same wire length becomes 'L2' and diameter 'd2' The ratio of resistances before and after stretching is ______.
For a transistor, αdc and βdc are the current ratios, then the value of `(beta_"dc"-delta_"dc")/(alpha_"dc".beta_"dc")`
In a p-n-p transistor circuit, the collector current is 10 mA. If 90% of the holes emitted from the emitter reach the collector, ______.
The base current in common emitter mode of the transistor changes by 10 µA. If the current gain of the transistor is 50, then change in collector current is ______.
The transfer ratio of a transistor is 50. The input resistance of the transistor when used in the CE configuration is 1K Ω. The peak value for an AC input voltage of 0.01 V of collector current is ______.
In a CE amplifier, the current gain is 80 and the emitter current is 9 mA. The base current is ______.
Define β
