Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why cannot we store AgNO3 solution in copper vessel?
उत्तर
Copper is above silver in the electrochemical series and is thus more reactive than silver. So, copper displaces silver from silver nitrate. Hence, we cannot store AgNO3 solution in copper vessel.
\[\ce{Cu + 2AgNO3 ->\underset{Silver}{2Ag} + \underset{Copper nitrate}{Cu(NO3)2}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive a relation between ΔH and ΔU for a chemical reaction. Draw neat labelled diagram of calomel electrode. Resistance and conductivity of a cell containing 0.001 M KCI solution at 298K are 1500Ω and 1.46x10-4 S.cm-1 respectively.
For the electrochemical cell:
M | M+ || X− | X,
E0(M+ | M) = 0.44 V, E0(X | X−) = 0.33 V
Which of the following is TRUE for this data?
What is the SI unit tor electrochemical equivalent?
A solution of Cu(NO3)2 is electrolyzed between platinum electrodes using 0.1 Faraday electricity. How many moles of Cu will be deposited at the cathode?
How many faradays of electricity are required for the following reaction to occur
\[\ce{MnO^-_4 -> Mn^2+}\]
Why is anode in galvanic cell considered to be negative and cathode positive electrode?
A copper electrode is dipped in 0.1 M copper sulphate solution at 25°C. Calculate the electrode potential of copper.
[Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Cu^{2+}|Cu}}}\] = 0.34 V]
For the cell \[\ce{Mg_{(s)}|Mg^{2+}_{( aq)}||Ag^+_{( aq)}|Ag_{(s)}}\], calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and maximum work that can be obtained during operation of cell.
Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Mg^{2+}|Mg}}}\] = −2.37 V and \[\ce{E^0_{{Ag^{+}|Ag}}}\] = 0.80 V
Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Λm | (a) S cm-¹ |
| (ii) ECell | (b) m-¹ |
| (iii) K | (c) S cm2 mol-¹ |
| (iv) G* | (d) V |
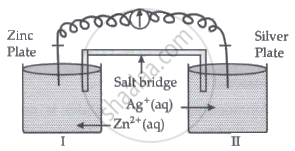
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
|
Oxidation-reduction reactions are commonly known as redox reactions. They involve transfer of electrons from one species to another. In a spontaneous reaction, energy is released which can be used to do useful work. The reaction is split into two half-reactions. Two different containers are used and a wire is used to drive the electrons from one side to the other and a Voltaic/Galvanic cell is created. It is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity. A salt bridge also connects to the half-cells. The reading of the voltmeter gives the cell voltage or cell potential or electromotive force. If \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] is positive the reaction is spontaneous and if it is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous and is referred to as electrolytic cell. Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as Cu2+. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis.
|
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode? (1)
- What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? (1)
- When does electrochemical cell behaves like an electrolytic cell? (1)
- (i) What will happen to the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ when Ecell = 0. (1)
(ii) Why does conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution? (1)
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution. (2)