Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why do the transition elements have higher enthalpies of atomisation?
Explain giving reason:
The enthalpies of atomisation of the transition metals are high.
उत्तर
They have higher enthalpies of atomization due to stronger interatomic interactions and consequently, stronger metallic bonding between atoms since they have a large number of unpaired electrons in their atoms.
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are interstitial compounds?
Account for the following:
Cu+2 salts are coloured, while Zn2+ salts are white.
In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which element has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
How would you account for the following:
The d1 configuration is very unstable in ions.
What are alloys?
Which one of the following ions is coloured?
The paramagnetic character in-3d-transition series elements increases-: up to Mn and then decreases.
Read the passage given below and answer the following question:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: Transition metals form protective oxide films.
Reason: Oxides of transition metals are always stoichiometric.
Assertion: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] iodide is not known.
Reason: \[\ce{Cu^2+}\] oxidises \[\ce{I^-}\] to iodine.
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
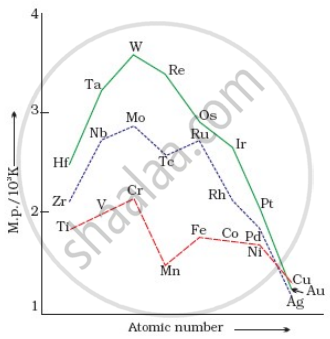
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
The element with atomic number 46 belongs to
Which of the following is non-metallic?
The spin magnetic moment of cobalt in the compound Hg [Co(SCN)4] is:-
Which of the following maxm magnetic moment?
On adding NaOH, solution to the aqueous solution of K2CrO7 the colour of the solution changes from
Why Zn, Cd and Hg are not called transition metals?
A transition element X has an electronic configuration [Ar]4s23d3. Predict its likely oxidation states.
A coordination compound has the formula \[\ce{CoCl3.4NH3}\]. It precipitates silver ions as AgCl and its molar conductance corresponds to a total of two ions.
Based on this information, answer the following question:
- Deduce the structural formula of the complex compound.
- Write the IUPAC name of the complex compound.
- Draw the geometrical isomers of the complex compound.
