Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why is the reactivity of all the three classes of alcohols with conc. \[\ce{HCl}\] and \[\ce{ZnCl2}\] (Lucas reagent) different?
उत्तर
The alcohol combine with \[\ce{HCl}\] to form protonated alcohol. The positive charge on oxygen weakens the C – O bond leading to its cleavage.
(i)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...............}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{...............}|\\
\ce{R - \underset{\bullet\bullet}{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - H + HCl ⇌[fast] R - \underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}^+ - H + Cl-}
\end{array}\]
(ii)

(iii)
\[\ce{R+ + Cl- ->[fast] RCl}\]
The rate-determining step in the above mechanism is (ii), which is a slow step reaction. The stability of carbocation will determine the reactivity of the reaction. Since the order of stability of carbocation is: Pri. < sec. < tert. Hence the order of formation of alkyl halide in the above reaction is pri. < sec. < tert.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
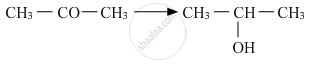
Ketones react with Grignard reagent to produce ____________.
Commercially carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols by converting them to the ______.
Magnesium wire continues to burn in the atmosphere of CO2 because
The reagent used for dehydration of an alcohol is
Most readily hydrolysed halide is:-
To synthesise 1.0 mole of 2-methylpropan-2-ol from Ethylethanoate ______ equivalents of CH3MgBr reagent will be required. (Integer value)
An aldehyde isomeric with allyl alcohol gives phenyl hydrazone. Pick out a ketone that too gives a phenyl hydrazone containing the same percentage of nitrogen.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
How are the following conversions carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide->2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
