Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a labelled ray-diagram, describe how a plane mirror forms an image of a point source of light placed in front of it. State the characteristics of the image formed in a plane mirror.
उत्तर

Consider a small object (a point source of light), placed in front of a plane mirror MM' (figure 1). The mirror will form an image I of the object O. This process of image formation is explained as follows:
The object O gives out light rays in all directions. Now, a ray of light OA, coming from the object O, is incident on the plane mirror at point A. OA gets reflected in the direction AX in accordance with the law of reflection, which states that the angle of reflection r1 equals the angle of incidence i1. Another ray of light OB, coming from the object O, strikes the mirror at point B. OB gets reflected in the direction BY, thus, making the angle of reflection r2 equal to the angle of incidence i2.
The two reflected rays AX and BY are divergent and cannot meet on the left side. Let's produce the reflected rays AX and BY backwards. They meet at a point I behind the mirror. When the reflected rays AX and BY enter the eye of a person at position E, the eye sees the rays in the direction in which they enter. So, the person looking into the mirror from position E sees the reflected rays as if they are coming from the point I behind the mirror. Thus, the point I is the image of the object O formed by the plane mirror.
The image produced by the plane mirror is virtual, laterally inverse and of the same size as the object.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The image formed by a plane mirror is :
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
(c) real, at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
What is meant by the 'angle of incidence' and the 'angle of refraction' for a ray of light?
Match the Following
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) white Light | (1) Convex mirror |
| (b) Refraction | (2) Concave mirror |
| (c) Virtual images | (3) refraction |
| (d) Real images | (4) spectrum |
| (e) Prism | (5) ray of light from glass to air |
The diagram (figure) given below shows two parallel rays 1 and 2 incident on (a) a concave mirror, (b) a convex mirror. Draw the reflected rays and mark the focus by the symbol F.
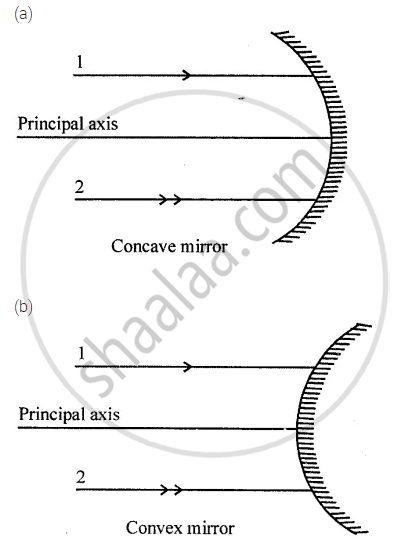
Write scientific reason.
The sun appears on the western horizon for some time after sunset.
A pencil when dipped in water in a glass tumbler appears to be bent at the interface of air and water. Will the pencil appear to be bent to the same extent, if instead of water we use liquids like, kerosene or turpentine. Support your answer with reason.
The phenomenon of light passing through the object is called ______.
When light passes from one medium to another the ray gets bent. This property of light is called ______.
How does the light travel?
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are ______.
