Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the transistor as an amplifier?
उत्तर
Working of an amplifier:
- The circuit of an amplifier using an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration is shown in the figure.
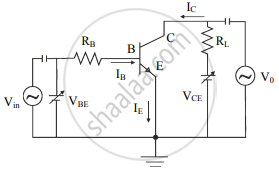
- When the input voltage Vin is not applied, applying the Kirchhoff’s law to the output loop, we can write, VCC = VCE + ICRL
- Similarly, for input loop,
VBB = VBE + IBRB - When the input AC signal is applied, Vin is not zero. Thus, the voltage drop across the input loop will now be,
VBB + Vin = VBE + IBRB + ΔIB (RB + ri) ....(1) - The AC signal applied adds the current of ΔIB to the original current flowing through the circuit. Therefore, the additional voltage drop in the input loop will be across resistor RB (= ΔIBRB) and across the input dynamic resistance of the transistor (= ΔIBri).
- From equation (1),
Vin = ΔIB (RB + ri)
As, RB is very small, we can consider,
Vin = ΔIBri - The changes in the base current IB cause changes in the collector current IC. This changes the voltage drop across the load resistance because VCC is constant. We can write,
ΔVCC = ΔVCE + RLIC = 0
∴ ΔVCE = -RLIC - The change in the output voltage ΔVCE is the output voltage Vo hence we can write,
Vo = ΔVCE = `beta`ACRLΔIB
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a common-base connection, a certain transistor has an emitter current of 10mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. Calculate the value of the base current.
Derive the relation between α and β.
In a transistor amplifier, IC = 5.5 mA , IE = 5.6 mA. The current amplification factor β is ______
Draw the circuit symbol of the PNP transistor.
The light emitted in an LED is due to
The output of the following circuit is 1 when the input ABC is
Give the Barkhausen conditions for sustained oscillations.
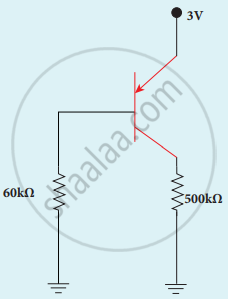
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
If l1, l2, l3 are the lengths of the emitter, base and collector of a transistor, then ____________.
In the study of transistor as an amplifier, the ratio of collector current to emitter current is 0.98 then the ratio of collector current to base current will be ______.
In switching circuit, transistor is in ON state. Values of IC and IB are 5.2 mA and 10 µA respectively and value of RC is 1 k`Omega`. If Vcc is at 5.5 V, then VCE is ______.
Ve, Vb, and Ve are emitter, base, and collector voltage respectively for npn transistor in CE mode. Amplifier works for the combination of biasing voltage equal to ______.
In an npn transistor, the base current is 100 µA and the collector current is 10 mA. The emitter current is ______.
In an npn transistor, the collector current is 24 mA. If 80% of electrons reach collector, its base current in mA is ______.
Which of the following regions of a transistors are, respectively, heavily dopped and lightly dopped?
For a common emitter configuration, if 'α' and 'β' have their usual meanings, the correct relationship between 'α' and 'β' is ______.
The current gain `alpha` of a transistor is 0.95. The change in collector current corresponding to a change of 0.4 mA in the base current in a common emitter arrangement is ______.
In a transistor, the thickness of the base region ____________.
In a transistor, doping level in base is increased slightly, the collector current and base current respectively ______.
In transistor amplifier, base-emitter junction is forward biased and collector emitter junction is reverse biased. The current gain is ______.
In the case of transistor, the relation between current ratios αdc and βdc is ______.
A change of 9.0 mA in the emitter current brings a change of 8.9 mA in the collector current. The value of current gain β will be ______.
A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of 50, an input impedance of 100Ω and an output impedance of 2000Ω. The power gain of the amplifier is ______.
In a p-n-p transistor circuit, the collector current is 10 mA. If 90% of the holes emitted from the emitter reach the collector, ______.
The reverse bias in a junction diode is changed from 8V to 13V, then the value of the current changes from 40μA to 60μA. The resistance of junction diode will be ______.
How is a transistor biased for operating it as amplifier?
