Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
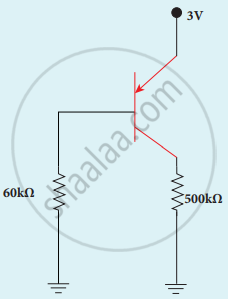
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
उत्तर
β = 50
VEB = 600 × 10−3 V
RB = 60 k Ω
RC = 500 k Ω
VB = VE – VEB
= 3 – 0.6
= 2.4 V
IB = `"V"_"B"/"R"_"B"`
= `2.4/(60 xx 10^9)`
= 0.04 × 10−3 A
IB = 40 µA
IC = β IB
= 50 × 40 × 10−6
IC = 2 mA
VC = IC RC = 500 IC
= 500 × 2 × 10−3
VEC = VE – VC
= 3 – 1
= 2 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive the relation between α and β.
Which method of biasing is used for operating a transistor as an amplifier?
For a transistor β =75 and IE = 7.5 mA. The value of α is ______
Give the Barkhausen conditions for sustained oscillations.
In an npn transistor, the base current is 100 µA and the collector current is 10 mA. The emitter current is ______.
In an npn transistor circuit, the collector current is 10 mA. If 90% of the electrons emitted reach the collector, the emitter current (IE) and base current (IB) are given by ____________.
In a silicon transistor, a change of 7.89 mA in the emitter current if produces a change of 7.8 mA in the collector current, then the base current must change by ____________.
A common emitter amplifier has a voltage gain of 50, an input impedance of 100Ω and an output impedance of 2000Ω. The power gain of the amplifier is ______.
A common emitter amplifier circuit built using an n-p-n transistor is shown in the figure. Its DC current gain is 300, RC = 4 kΩ and VCC = 20 V. What is the minimum base current for VCE to reach saturation?
In a CE amplifier, the current gain is 80 and the emitter current is 9 mA. The base current is ______.
