Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
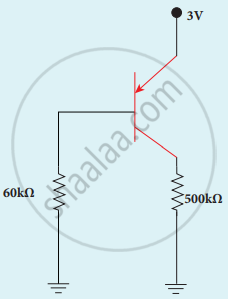
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
उत्तर
β = 50
VEB = 600 × 10−3 V
RB = 60 k Ω
RC = 500 k Ω
VB = VE – VEB
= 3 – 0.6
= 2.4 V
IB = `"V"_"B"/"R"_"B"`
= `2.4/(60 xx 10^9)`
= 0.04 × 10−3 A
IB = 40 µA
IC = β IB
= 50 × 40 × 10−6
IC = 2 mA
VC = IC RC = 500 IC
= 500 × 2 × 10−3
VEC = VE – VC
= 3 – 1
= 2 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The common-base DC current gain of a transistor is 0.967. If the emitter current is 10mA. What is the value of base current?
Explain the working of the PNP transistor?
Draw the circuit symbol for NPN and PNP transistors. What is the difference in the Emitter, Base, and Collector regions of a transistor?
Describe the function of a transistor as an amplifier with the neat circuit diagram. Sketch the input and output wave forms.
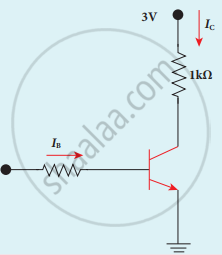
Assuming VCEsat = 0.2 V and β = 50, find the minimum base current (IB) required to drive the transistor given in the figure to saturation.
Least doped region in a transistor ____________.
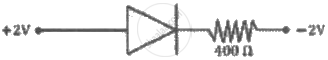
For an ideal diode, the current in the following arrangement is ______.
The reverse bias in a junction diode is changed from 8V to 13V, then the value of the current changes from 40μA to 60μA. The resistance of junction diode will be ______.
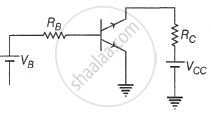
A common emitter amplifier circuit built using an n-p-n transistor is shown in the figure. Its DC current gain is 300, RC = 4 kΩ and VCC = 20 V. What is the minimum base current for VCE to reach saturation?
The collector current in a common-emitter transistor amplifier is 4 mA. When the base current is increased by 20 µA, the collector current increases to 6 mA. The current gain is ______.
