Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the circuit symbol for NPN and PNP transistors. What is the difference in the Emitter, Base, and Collector regions of a transistor?
उत्तर
The circuit symbols of the two types of transistors:
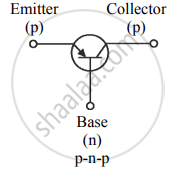
Figure (a)

Figure (b)
The difference in the Emitter (E), the Base (b), and the Collector (C) are as follows:
- Emitter: It is a thick heavily doped layer. This supplies a large number of majority carriers for the current flow through the transistor
- Base: It is the thin, lightly doped central layer.
- Collector: It is a thick and moderately doped layer. Its area is larger than that of the emitter and the base. This layer collects a major portion of the majority of carriers supplied by the emitter. The collector also helps dissipation of any small amount of heat generated.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are the emitter, the base, and the collector of a BJT doped differently?
In a common base configuration, the transistor has an emitter current of 10 mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. The value of base current is ______
For a transistor β =75 and IE = 7.5 mA. The value of α is ______
Explain the working of the PNP transistor?
With the help of a neat diagram, explain the working of the npn transistor?
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the transistor as an amplifier?
The principle based on which a solar cell operates is ____________.
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
Transistor functions as a switch. Explain.
Describe the function of a transistor as an amplifier with the neat circuit diagram. Sketch the input and output wave forms.
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
In a common emitter amplifier, the input resistance is 1000 Ω, the peak value of Input signal voltage is 5 mV, and β = 60. The peak value of output current is
For a transistor, the current ratio 'βdc' is defined as the ratio of ______.
Least doped region in a transistor ____________.
In switching circuit, transistor is in ON state. Values of IC and IB are 5.2 mA and 10 µA respectively and value of RC is 1 k`Omega`. If Vcc is at 5.5 V, then VCE is ______.
Ve, Vb, and Ve are emitter, base, and collector voltage respectively for npn transistor in CE mode. Amplifier works for the combination of biasing voltage equal to ______.
If `alpha`-current gain of a transistor is 0.98. What is the value of `beta`- current gain of the transistor?
In switching circuit, transistor is in ON state, values of IE and lB are 10 mA and 0.8 mA respectively and RL is 2 k`Omega`. If VCE is 7.6 V, then VCC is ____________.
For a common emitter configuration, if 'α' and 'β' have their usual meanings, the correct relationship between 'α' and 'β' is ______.
A pnp transistor is used in common-emitter mode. If a change of 40 µA in base current brings a change of 2 µA in collector current with 0.04 V in base-emitter voltage, then the input resistance is ____________.
In a transistor, the thickness of the base region ____________.
In the common-emitter configuration of a transistor, the current gain is more than 1 because [lb, le, and lc are base, emitter, and collector currents respectively] ______
A conducting wire has length 'L1' and diameter 'd1'. After stretching the same wire length becomes 'L2' and diameter 'd2' The ratio of resistances before and after stretching is ______.
The current amplification factor for a transistor in its common emitter mode is 50. The current amplification factor in the common base mode of the transistor is ______.
How is a transistor biased for operating it as amplifier?
In a CE amplifier, the current gain is 80 and the emitter current is 9 mA. The base current is ______.
Define α.
