Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of a neat diagram, explain the working of the npn transistor?
उत्तर
Working of n-p-n transistor:
- The majority of charge carriers in the emitter of the n-p-n transistor are electrons.
- A typical biasing of a transistor is shown in figure (a). In this, the emitter-base junction is forward biased while the collector-base junction is reverse biased.

Figure (a) - At the instant when the EB junction is forward biased, electrons in the emitter region have not entered the base region as shown in figure (b).
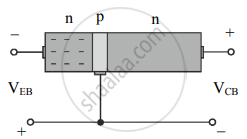
Figure (b) - When the biasing voltage VBE is greater than the barrier potential (0.6 – 0.7 V for Si transistors), many electrons enter the base region and form the emitter current IE as shown in figure (c).
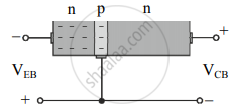
Figure (c) - These electrons can either flow through the base circuit and constitute the base current (IB), or they can also flow through the collector circuit and contribute towards the collector current (IC).
- The base is thin and lightly doped, the base current is only 5% of IE.
- Electrons injected from the emitter into the base diffuse into the collector-base depletion region due to the thin base region. When the electrons enter the collector-base depletion region, they are pushed into the collector region by the electric field at the collector-base depletion region. The collector current (IC) flows through the external circuit as shown in figure (d). The collector's current IC is about 95% of IE.
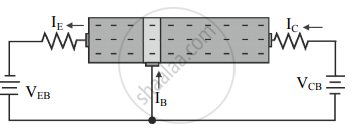
Figure (d)
From the figure, we can conclude that IE = IB + IC Since the base current IB is very small we can write IC ≈ IE.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a common-base connection, a certain transistor has an emitter current of 10mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. Calculate the value of the base current.
Derive the relation between α and β.
Which method of biasing is used for operating a transistor as an amplifier?
For a transistor IC = 15 mA, IB = 0.5 mA. What is the current amplification factor?
Draw the circuit symbol for NPN and PNP transistors. What is the difference in the Emitter, Base, and Collector regions of a transistor?
Explain the need for a feedback circuit in a transistor oscillator.
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
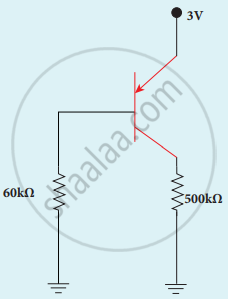
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
In a common emitter amplifier, the input resistance is 1000 Ω, the peak value of Input signal voltage is 5 mV, and β = 60. The peak value of output current is
For a transistor, the current ratio 'βdc' is defined as the ratio of ______.
If `alpha`-current gain of a transistor is 0.98. What is the value of `beta`- current gain of the transistor?
In an npn transistor, the collector current is 24 mA. If 80% of electrons reach collector, its base current in mA is ______.
In a transistor in CE configuration, the ratio of power gain to voltage gain is ____________.
For a common emitter configuration, if 'α' and 'β' have their usual meanings, the correct relationship between 'α' and 'β' is ______.
In a silicon transistor, a change of 7.89 mA in the emitter current if produces a change of 7.8 mA in the collector current, then the base current must change by ____________.
In a transistor, doping level in base is increased slightly, the collector current and base current respectively ______.
In transistor amplifier, base-emitter junction is forward biased and collector emitter junction is reverse biased. The current gain is ______.
In common emitter amplifier, a change of 0.2 mA in the base current causes a change of 5 mA in the collector current. If input resistance is 2K `Omega` and voltage gain is 75, the load resistance used in the circuit is ______.
A transistor having α = 0.8 is connected in a common emitter configuration. When the base current changes by 6 mA, the change in collector current is ______
In the common-emitter configuration of a transistor, the current gain is more than 1 because [lb, le, and lc are base, emitter, and collector currents respectively] ______
The reverse bias in a junction diode is changed from 8V to 13V, then the value of the current changes from 40μA to 60μA. The resistance of junction diode will be ______.
A common emitter amplifier circuit built using an n-p-n transistor is shown in the figure. Its DC current gain is 300, RC = 4 kΩ and VCC = 20 V. What is the minimum base current for VCE to reach saturation?
The base current in common emitter mode of the transistor changes by 10 µA. If the current gain of the transistor is 50, then change in collector current is ______.
Explain the working of the n-p-n transistor in a common base configuration.
How is a transistor biased for operating it as amplifier?
Define peak value of alternating signal.
Define α.
Define β
