Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
उत्तर

Static characteristics of a NPN transistor in common emitter configuration
- The circuit to study the static characteristics of NPN transistor is given in figure
- Bias supply voltages VBB and VCC bias, base-emitter junction and collector-emitter junction.
- Junction potentials are VBE and YCE
- R1 and R2 are used to vary base and collector currents respectively.
1. Input Characteristics:
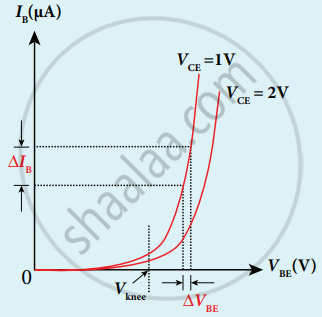
- Input Characteristics curve gives the relationship between IB and VBE at constant VCE
- For constant collector-emitter voltage VCE, Base emitter voltage VBE increases for corresponding Base current IB which is recorded and graph is ploted.
- The curve looks like forwarding characteristics.
- Beyond knee voltage base current increases with an increase in base-emitter voltage for silicon 0.7 V and for Germanium 0.3 V.
- Increase in VCE decreases IB. This shifts the curves outward.
- Input resistance Ri = `((Δ"V"_"BE")/(Δ"I"_"B"))_("V"_"CE")`
2. Output characteristics:

- The output characteristics give the relation between ∆IC with respect to ∆VCE at constant IB
- Initially base current IB is set to a particular value. Increasing collector-emitter voltage VCE corresponding collector current IC increases. A graph is plotted.
- Output resistance Ro = `((Δ"V"_"CE")/(Δ"I"_"C"))_"IB"`
The four important regions in the output characteristics are:
- Saturation region: When VCE increased above 0V, IC increases rapidly almost independent of IB called knee voltage Transistor operated above this knee voltage.
- Cut-off region: A small IC exists even after IB is reduced to zero. This current is due to the presence of minority carriers across the collector-base junction and the surface leakage current (ICEO). This region is called the cut-off region.
- Active region: In this region emitter-base junction is forward bias, collector-base junction is reverse bias. Transistors in this region can be used for voltage, current and power amplification.
- breakdown region: If VCE is increased beyond rated value, given Ic increases enormously leading to junction breakdown of the transistor. This avalanche breakdown can damage.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a BJT, the largest current flow occurs ______.
With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the transistor as an amplifier?
In the symbol for a transistor, the arrow head points in the direction of the ____________.
If `alpha`-current gain of a transistor is 0.98. What is the value of `beta`- current gain of the transistor?
In an npn transistor, the base current is 100 µA and the collector current is 10 mA. The emitter current is ______.
Which of the following regions of a transistors are, respectively, heavily dopped and lightly dopped?
In a common emitter amplifier circuit using an n-p-n transistor, the phase difference between the input and the output voltages will be: ____________.
A transistor is connected in C - E mode. If collector current is 72 × 10-5 A and α = 0.96, then base current will be ______.
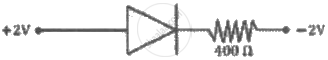
For an ideal diode, the current in the following arrangement is ______.
For a transistor, αdc and βdc are the current ratios, then the value of `(beta_"dc"-delta_"dc")/(alpha_"dc".beta_"dc")`
