Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
उत्तर

Static characteristics of a NPN transistor in common emitter configuration
- The circuit to study the static characteristics of NPN transistor is given in figure
- Bias supply voltages VBB and VCC bias, base-emitter junction and collector-emitter junction.
- Junction potentials are VBE and YCE
- R1 and R2 are used to vary base and collector currents respectively.
1. Input Characteristics:
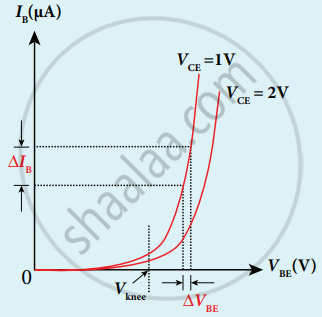
- Input Characteristics curve gives the relationship between IB and VBE at constant VCE
- For constant collector-emitter voltage VCE, Base emitter voltage VBE increases for corresponding Base current IB which is recorded and graph is ploted.
- The curve looks like forwarding characteristics.
- Beyond knee voltage base current increases with an increase in base-emitter voltage for silicon 0.7 V and for Germanium 0.3 V.
- Increase in VCE decreases IB. This shifts the curves outward.
- Input resistance Ri = `((Δ"V"_"BE")/(Δ"I"_"B"))_("V"_"CE")`
2. Output characteristics:

- The output characteristics give the relation between ∆IC with respect to ∆VCE at constant IB
- Initially base current IB is set to a particular value. Increasing collector-emitter voltage VCE corresponding collector current IC increases. A graph is plotted.
- Output resistance Ro = `((Δ"V"_"CE")/(Δ"I"_"C"))_"IB"`
The four important regions in the output characteristics are:
- Saturation region: When VCE increased above 0V, IC increases rapidly almost independent of IB called knee voltage Transistor operated above this knee voltage.
- Cut-off region: A small IC exists even after IB is reduced to zero. This current is due to the presence of minority carriers across the collector-base junction and the surface leakage current (ICEO). This region is called the cut-off region.
- Active region: In this region emitter-base junction is forward bias, collector-base junction is reverse bias. Transistors in this region can be used for voltage, current and power amplification.
- breakdown region: If VCE is increased beyond rated value, given Ic increases enormously leading to junction breakdown of the transistor. This avalanche breakdown can damage.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are the emitter, the base, and the collector of a BJT doped differently?
The common-base DC current gain of a transistor is 0.967. If the emitter current is 10mA. What is the value of base current?
In a common-base connection, a certain transistor has an emitter current of 10mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. Calculate the value of the base current.
Transistor functions as a switch. Explain.
A transistor has a voltage gain A. If the amount βA of its output is applied to the input of the transistor, then the transistor becomes oscillator, when ______.
In an npn transistor, the base current is 100 µA and the collector current is 10 mA. The emitter current is ______.
For a common emitter configuration, if 'α' and 'β' have their usual meanings, the correct relationship between 'α' and 'β' is ______.
In a transistor, a change of 8.0 mA in the emitter current produces a change of 7.8 mA in the collector current. Then change in the base current is ____________.
For a transistor, αdc and βdc are the current ratios, then the value of `(beta_"dc"-delta_"dc")/(alpha_"dc".beta_"dc")`
The transfer ratio of a transistor is 50. The input resistance of the transistor when used in the CE configuration is 1K Ω. The peak value for an AC input voltage of 0.01 V of collector current is ______.
