Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write answers in ‘one’ or ‘two’ paras each.
What are the main determinants of aggregate demand?
उत्तर
Aggregate demand is the summation of consumption expenditure (C), investment expenditure (I), government expenditure (G) and net earnings from foreign transactions (X – M).
where, X is exports and M is imports
AD = C + I + G + (X – M)
The following are the determinants of aggregate demand:
i. Consumption expenditure (C): Consumption expenditure refers to the total expenditure incurred by all the households in an economy on different types of final goods and services in order to satisfy their wants. There are two types of consumption expenditure - Autonomous consumption expenditure and Induced consumption expenditure.
ii. Investment expenditure (I): Private investment expenditure refers to the planned (ex-ante) total expenditure incurred by all the private investors on creation of capital goods such as expenditure incurred on new machinery, tools, buildings, raw materials etc. Broadly, investment can be categorised into two types- Autonomous investment expenditure and Induced investment expenditure.
iii. Government expenditure (G): Government expenditure refers to the total planned expenditure incurred by the government on consumption and investment purposes to enhance the welfare of the society and to achieve higher economic growth rates. The government expenditure comprises of both investment expenditure as well as consumption expenditure.
iv. Net exports (X – M): Net exports of a country refers to the difference between the demand for domestically produced goods and services by the rest of the world (exports) and the demand for goods and services produced abroad by the residents of that country.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Demand for necessaries is................
(elastic / inelastic / infinitely elastic / unitary elastic)
When does ‘decrease’ in demand take place?
What is meant by inelastic demand?
Explain the problem of what to produce.
Demand for a good is termed inelastic through the expenditure approach when if (choose the correct alternative)
a) Price of good falls, expenditure on it rises
b) Price of the good falls, expenditure in it falls
c) Price of the good falls, expenditure on it remains unchanged
d) Price of the good rises, expenditure in it falls
Distinguish between ‘increase in demand’ and increase in quantity demanded of a good.
Demand deposits include (choose the correct alternative)
(a) Saving account deposits and fixed deposits
(b) Saving account deposits and current account deposits
(c) Current account deposits and fixed deposits
(d) All types of deposits
If due to fall in the price of good X, demand for good Y rises, the two goods are : (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Substitutes
b. Complements
c. Not related
d. Competitive
When is demand called perfectly inelastic?
Give one reason for shift in demand curve.
Define or explain the following concept :
Effective demand .
Fill in the blank using proper alternative given in the bracket:
Perfectly inelastic demand curve is.....................................................
Write short answer for the following question.
Explain the Law of Demand.
Fill in the blank using proper alternatives given in the bracket:
Demand for salt is ...............
Write whether the following statement is True or False:
Demand for commodities depends upon various factors.
Define or explain the concept of Demand schedule.
Write Explanatory answer.
State and explain the law of demand with its exception.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
When price of commodity rises, the demand for it ______________.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below:
Indirect demand is also known as _____________ demand.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
When demand increases, the demand curve shifts to the left.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE
Quantity demanded varies directly with price.
Define or explain the following concept:
Derived demand
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand curve slopes downward from left to right.
Give reason or explain the following statement.
Demand for factors of production is derived demand.
Answer the following question
What do you mean by demand?
Distinguish between substitute goods and complementary goods, with examples.
If the income of a consumer increases, discuss briefly its likely impact on the demand for a inferior good, Good X.
Choose the correct answer from given options
In the given figure X1Y1 and X2Y2 are Production Possibility Curves in two different periods T1 and T2 respectively for Good X and Good Y. A1 and A2 represent actual outputs and P1 and P2 represent potential outputs respectively in the two times periods.
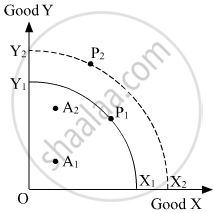
The change in actual output of Goods X and Y over the two periods would be represented by a movement from __________.
In case of ______ supply curve is a vertical straight line parallel to Y-axis.
There is a sudden change in climatic conditions resulting in hot weather. Assuming no change in the price of the cold drinks, it will lead to ______
Increase in price of substitute goods leads to ______
From the set of statements given in Column A and Column B, choose the correct pair of statement:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Reduction of pollution | (a) Microeconomics |
| 2. Problems due to unemployment | (b) Microeconomics |
| 3. Shift in the demand curve | (c) Microeconomics |
| 4. Government expenditure on building of roads | (d) Microeconomics |
Are the concepts of demand for domestic goods and domestic demand for goods the same?
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Utility | (a) Bread and butter |
| (2) Normal Goods | (b) Rise in price |
| (3) Contraction in demand | (c) Capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants. |
| (4) Complementary goods | (d) Positively related |
If the increase in demand is greater than the increase in supply, then equilibrium price will ______
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Budget Line | (a) Normal goods |
| (2) Bajra | (b) Inferior goods |
| (3) Consumer equilibrium | (c) Luxurious goods |
| (4) Elastic Demand | (d) M = Px*x + py*y |
What will be the effect on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity when income increases in case of normal goods?
Which of the following can cause an increase in demand:
Which of the following have elastic demand?
Identify the two cost curves which start from the same point on the Y-axis.
Aggregate demand can be decreased by:
Which of the following statements is correct with respect to the correction of Excess Demand?
Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is false?
Read the following news report and answer the Q.97-Q.100 on the basis of the same:
The quantity of a commodity that a consumer is willing to buy and is able to afford, given the prices of goods and the consumer's tastes and preferences is called demand for the commodity. Whenever one or more of these variables change, the quantity of the good Chosen by the consumer is likely to change as well. The relation between the consumer's optimal choice of the quantity of a good and its price is very important and this relation is called the demand function. Thus, the consumer's demand function for a good gives the amount of the good that the consumer chooses at different levels of its price when the other things remain.
What is meant by the contraction of demand?
The demand curve of a firm under monopoly is ______
Which of the following is the reason behind the downward slope of demand option?
When the price of the commodity has changed the demand for the commodity changes in ______
Demand deposits include:
Which of the following statements is true?
