Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write main differences between the properties of white phosphorus and red phosphorus.
उत्तर १
| White phosphorus | Red Phosphorus |
| It is a soft and waxy solid. It possesses a garlic smell. | It is a hard and crystalline solid, without any smell. |
| It is poisonous. | It is non-poisonous. |
| It is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulphide. | It is insoluble in both water and carbon disulphide. |
| It undergoes spontaneous combustion in air. | It is relatively less reactive. |
|
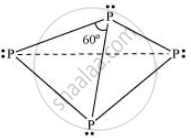
In both solid and vapour states, it exists as a P4 molecule
|
It existIt exists as a chain of tetrahedral P4 units.s as a chain of tetrahedral P4 units.
|
उत्तर २
| White phosphorus | Red Phosphorus |
| It is a soft and waxy solid. It possesses a garlic smell. | It is a hard and crystalline solid, without any smell. |
| It is poisonous. | It is non-poisonous. |
| It is insoluble in water but soluble in carbon disulphide. | It is insoluble in both water and carbon disulphide. |
| It undergoes spontaneous combustion in air. | It is relatively less reactive. |
|
In both solid and vapour states, it exists as a P4 molecule
|
It existIt exists as a chain of tetrahedral P4 units.s as a chain of tetrahedral P4 units.
|
उत्तर ३
| Property | White Phosphorus | Red Phosphorus | |
| 1 | State | Translucent | Brittle, substance |
| 2 | Colour | White get yellowish on exposure to light | Red |
| 3 | Odour | Garlic like odour | Odourless |
| 4 | hardness | Soft like wax and can be cut by knife | hard |
| 5 | Poisonous nature | Poisonous | Non-poisonous |
| 6 | Solubility | Soluble in `CS_2` | Insoluble in `CS_2` |
| 7 | Chemiluminescence | Glow in dark | Does not glow in dark |
| 8 | Density | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| 9 | Reactivity | Very reactive | Less reactive |
| 10 | Action of oxygen | Burm with greenish glow | Combine with `O_2` only on heating to form `P_4O_10` |
Structure of white phosphorus and red phosphorus.

White Phosphorus

Red Phosphorus
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain how does nitrogen exhibit anomalous behaviour amongst group 15 elements.
Give reasons for the following : (CH3)3 P = O exists but (CH3)3 N = O does not.
Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of Group 15 elements?
Discuss the general characteristics of Group 15 elements with reference to their electronic configuration, oxidation state, atomic size, ionisation enthalpy and electronegativity.
Among the hydrides of Group-15 elements, which have the maximum reducing character?
Give reasons When Cl2 reacts with the excess of F2, ClF3 is formed and not FCl3.
Give a reason for the following:
E° value for (Mn2+|Mn) is negative whereas for (Cu2+|Cu) is positive.
[Ar]3d104s24p3 is the electronic configuration of ____________.
The element which forms oxides in all oxidation states varying from +1 to +5 is ____________.
Among the following, which one is a wrong statement.
The correct order of oxidising power is:
If chlorine gas is passed through hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are :
(i) 0 to +5
(ii) 0 to +3
(iii) 0 to –1
(iv) 0 to +1
Among the following, identify the species with an atom in +6 oxidation state
The elements which are characterized by the outer electronic configuration ns1 to ns2 np6 are collectively called
When a colourless gas is passed through bromine water it decolorise, The gas is:-
Chemical nature of the nitrogen oxide compound obtained from a reaction of concentrated nitric acid and P4O10 (in 4 : 1 ratio) is ______.
A ·group 15 element, which is a metal and forms a hydride with strongest reducing power among group 15 hydrides. The element is ______.