Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
उत्तर
\[\ce{Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4 ->[Discharge] 2PbSO4 + 2H2O}\]
Density of electrolyte decreases because water is formed and sulphuric acid consumed as the product during discharge of the battery.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Resistance of conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 100 ohms. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 520 ohms, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution. [Given: Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m-1 .]
Define limiting molar conductivity.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
The conductivity of sodium chloride at 298 K has been determined at different concentrations and the results are given below:
| Concentration/M | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.020 | 0.050 | 0.100 |
| 102 × κ/S m−1 | 1.237 | 11.85 | 23.15 | 55.53 | 106.74 |
Calculate `∧_"m"`for all concentrations and draw a plot between `∧_"m"`and `"c"^(1/2)`. Find the value of `∧_"m"^0`.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Why on dilution the m Λm of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] increases very fast, while that of \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] increases gradually?
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.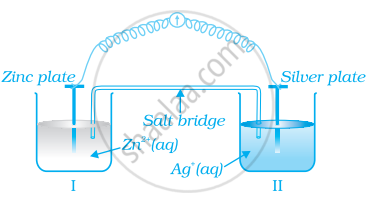
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
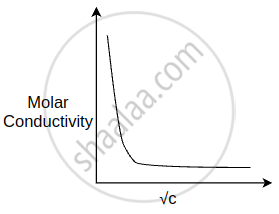
The electrolyte X is ______.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
