Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words: solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
उत्तर
To make tea, we will use the following steps:
- Take 100 mL of water, which will serve as the solvent.
- Boil water on a gas stove.
- Add one teaspoon of sugar, which acts as a solute.
- Sugar is soluble in water, therefore it dissolves in water and forms a solution.
- Now add roughly half a teaspoon of tea leaves that are insoluble in water.
- Boil the contents for 4 to 5 minutes, then add a half cup of milk and continue to boil for 2-3 minutes.
- Filter the tea using a sieve.
- Tea leaves will be left as residue, and tea will be extracted as filtrate.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Pragya tested the solubility of three different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
| Substance dissolved | Temperature in K | ||||
| 283 | 293 | 313 | 333 | 353 | |
| Solubility | |||||
| Potassium nitrate | 21 | 32 | 62 | 106 | 167 |
| Sodium chloride | 36 | 36 | 36 | 37 | 37 |
| Potassium chloride | 35 | 35 | 40 | 46 | 54 |
| Ammonium chloride | 24 | 37 | 41 | 55 | 66 |
- What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 50 grams of water at 313 K?
- Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools? Explain.
- Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. What salt has the highest solubility at this temperature?
- What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt?
The component present in a lesser amount, in a solution, is called ______
Define the term: Solution
Give an example of a solid in a liquid.
Smoke and fog both are aerosols. In what way are they different?
Can a solution be heterogeneous?
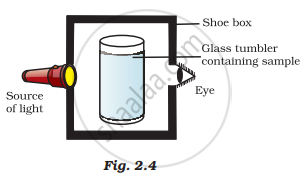
A group of students took an old shoebox and covered it with black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and making another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in Fig.2.4. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it?
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.
(b) The same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.
(c) Can you suggest two more solutions that would show the same effect as shown by the milk solution?
During an experiment, the students were asked to prepare a 10% (Mass/Mass) solution of sugar in water. Ramesh dissolved 10g of sugar in 100g of water while Sarika prepared it by dissolving 10g of sugar in water to make 100g of the solution.
(a) Are the two solutions of the same concentration
(b) Compare the mass % of the two solutions.
______ is the major difference between true solutions, suspensions, and colloids.
What is the solvent?
